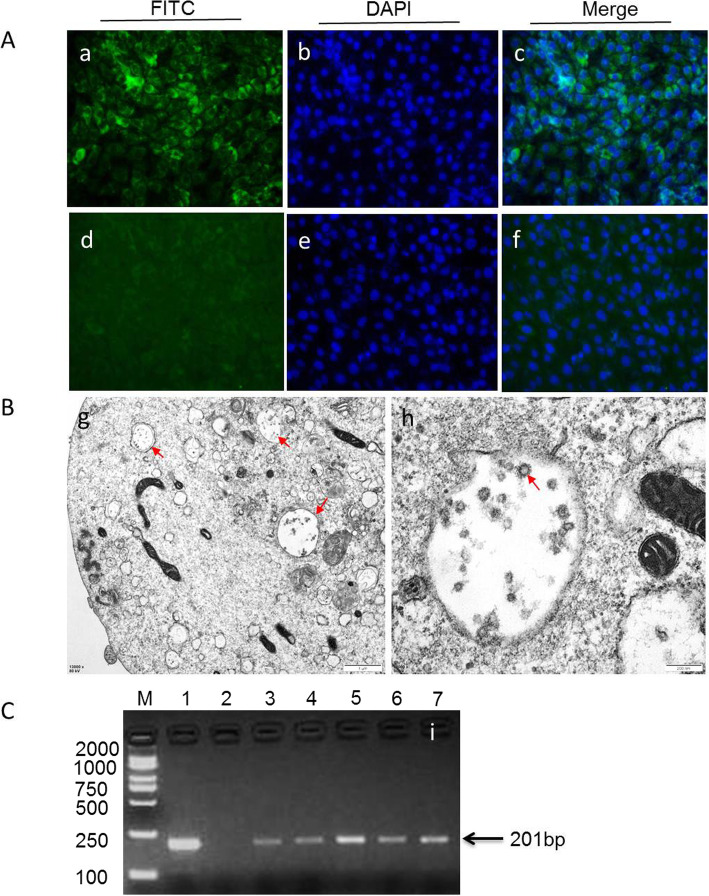
Fig. 1.
The isolated BVDV strains were confirmed by immunofluorescence, RT-PCR and transmission electron microscope, respectively. a BVDV-infected (a-c) or negative control MDBK cells (d-f) were examined by immunofluorescence using polyclonal antibodies against BVDV E2 protein. b The typical viral particles in the cytoplasm of infected MDBK cell(g, red arrow). The viral particles were measured approximately 60 nm in diameter and occurred as clusters inside vesicles(h, red arrow). c The BVDV strains were detected by 5’UTR RT-PCR (201 bp). Representative electron microscopic image of field BVDV isolates (i). lane M:weight size marker (2000 bp,1000 bp, 750 bp, 500 bp, 250 bp,100 bp), lane 1: positive control; lane 2: negative control, lanes 3–7: BVDV strains isolated from clinical serum samples