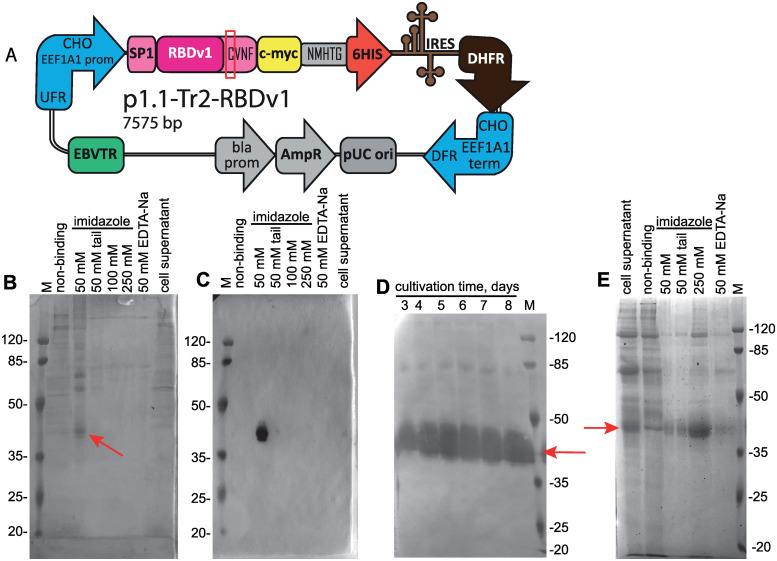
Fig 1. Map of the p1.1-Tr2-RBDv1 plasmid, purification of the RBDv1 protein its extended batch cultivation.
A—Scheme of p1.1-Tr2-RBDv1 expression plasmid. CHO EEF1A1 UFR–upstream flanking area of the EEF1A1 gene (EEF1A1 gene promoter, flanked with 5’ untranslated region), DFR–downstream flanking area (EEF1A1 gene terminator and polyadenylation signal, flanked with 3’ untranslated region); IRES–encephalomyocarditis virus internal ribosome entry site; DHFR–ORF of the dihydrofolate reductase gene of Mus musculus, pUC ori–replication origin; AmpR and bla prom–ampicillin resistance gene and the corresponding promoter; EBVTR–fragment of the long terminal repeat from the Epstein-Barr virus; SP1 –signal peptide, RBDv1 –RBD ORF, amino acids from natural Spike protein sequence (SP1 and CVNF) are shown in pink color; unpaired cysteine is surrounded by a red rectangle; c-myc and 6HIS–C-terminal fusion tags, NMHTG—linker peptide sequence. B–SDS-PAGE analysis of the RBDv1 purification by the IDA-Ni chromatography resin. Protein was obtained from the cell culture at 2 μM MTX selection pressure, cell supernatant and non-binding proteins fractions applied without ultrafiltration, 10 μl/lane, column elution fractions applied as 10 μl from 5 ml total, concentration factor 30x. Position of the target protein band is depicted by arrow. Molecular masses are given in kDa. C–Western blot analysis of the RBDv1 purification by the IDA-Ni chromatography resin. Anti c-myc primary antibodies, lanes load same to panel B. D—Western blot analysis of the extended batch cultivation of the RBDv1 2 μM MTX cell population, 2 μl of cell supernatant/lane. E—SDS-PAGE analysis of the RBDv1 purification by the Ni-NTA chromatography resin. Lane loads same to panel B.