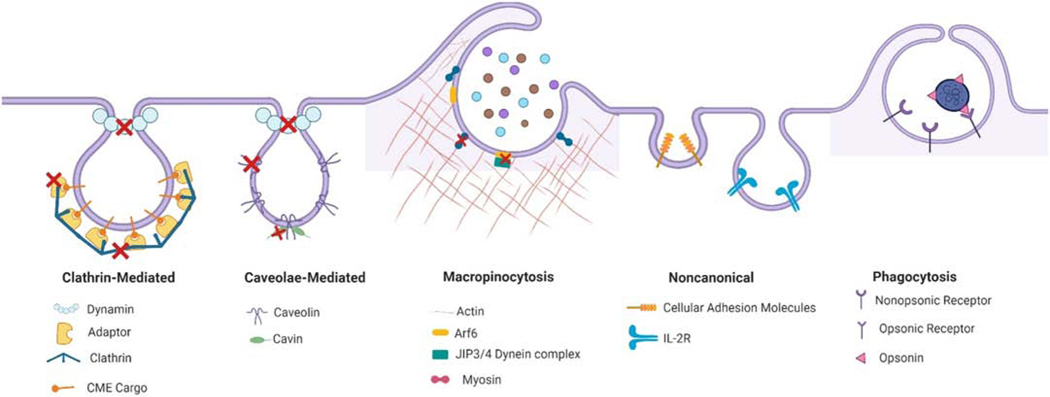
Figure 1. Schematic summary of the cellular uptake mechanisms and genetic targets which have been utilized to manipulate endocytotic pathways involved in drug delivery.
Red crosses mark the genetic targets used to manipulate the different endocytotic pathways. Targeting of clathrin, adaptor proteins and dynamin all affect clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Genetic methods targeting different members of the caveolin or cavin family and dynamin also disrupt caveolaer-mediated endocytosis in different tissues. Targeting of members of the myosin family, JIP3/4, and Arf6 have been shown to interfere with macropinocytosis. Less consensus exists on the role of specific molecular effectors of the other endocytosis pathways indicated as useful for drug delivery. This schematic was created using BioRender.com