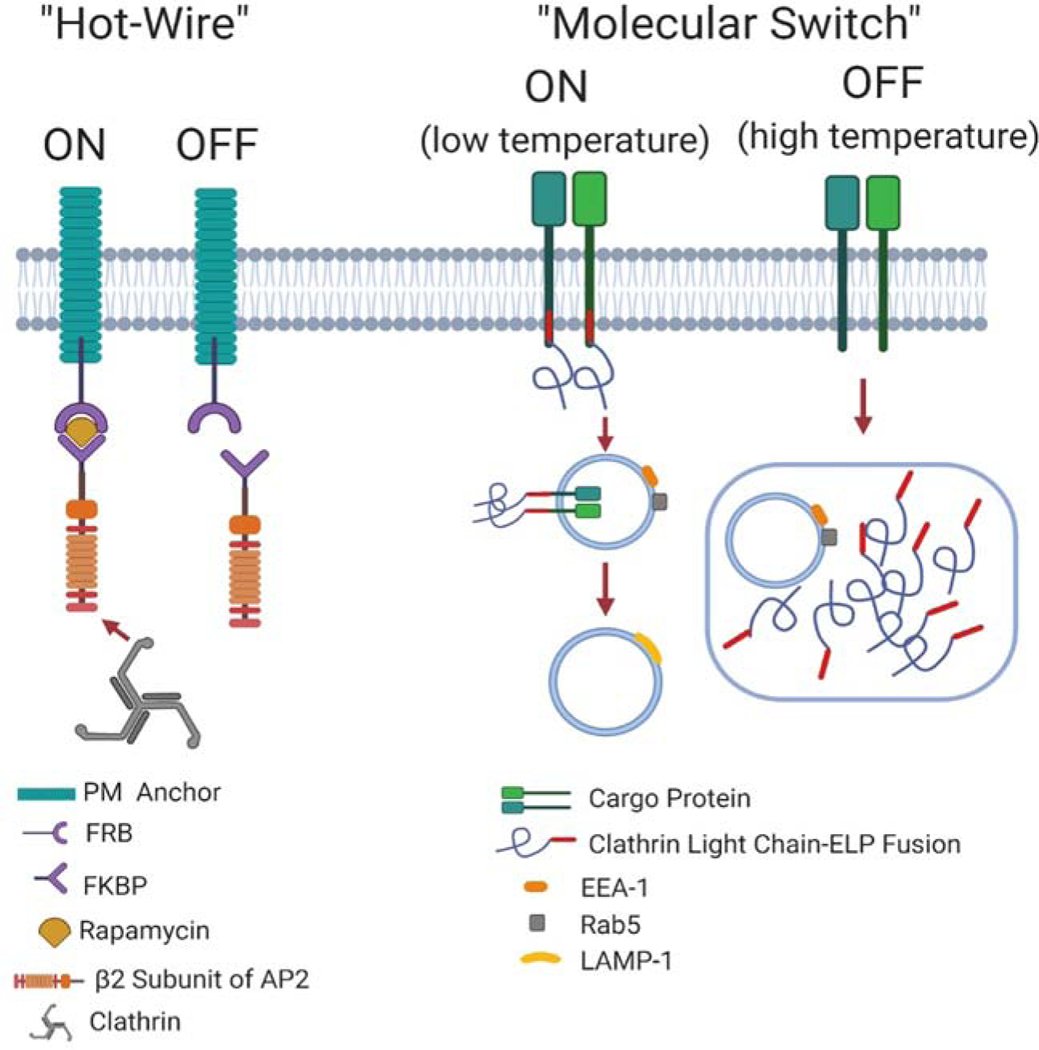
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of protein engineering methods used to study CME.
For the “Hot-Wire” method, CME is turned on in the presence of rapamycin. The FK506 binding protein (FKBP)-AP2 complex can be recruited to the plasma membrane in the presence of rapamycin through binding to rapamycin binding protein (FRB) which is anchored to the plasma membrane through fusion to a plasma membrane protein. Clathrin can be further recruited to initiate CME. In the absence of rapamycin, the FKBP-AP2 complex cannot bind to FRB. Thus, clathrin will not be recruited to the plasma membrane and CME is turned off. For the ”Molecular Switch ”method, at low temperature, CLC-ELP remains soluble and maintains normal CME function. At high temperature, CLC-ELP forms microdomains and shuts off CME. This schematic was created using BioRender.com