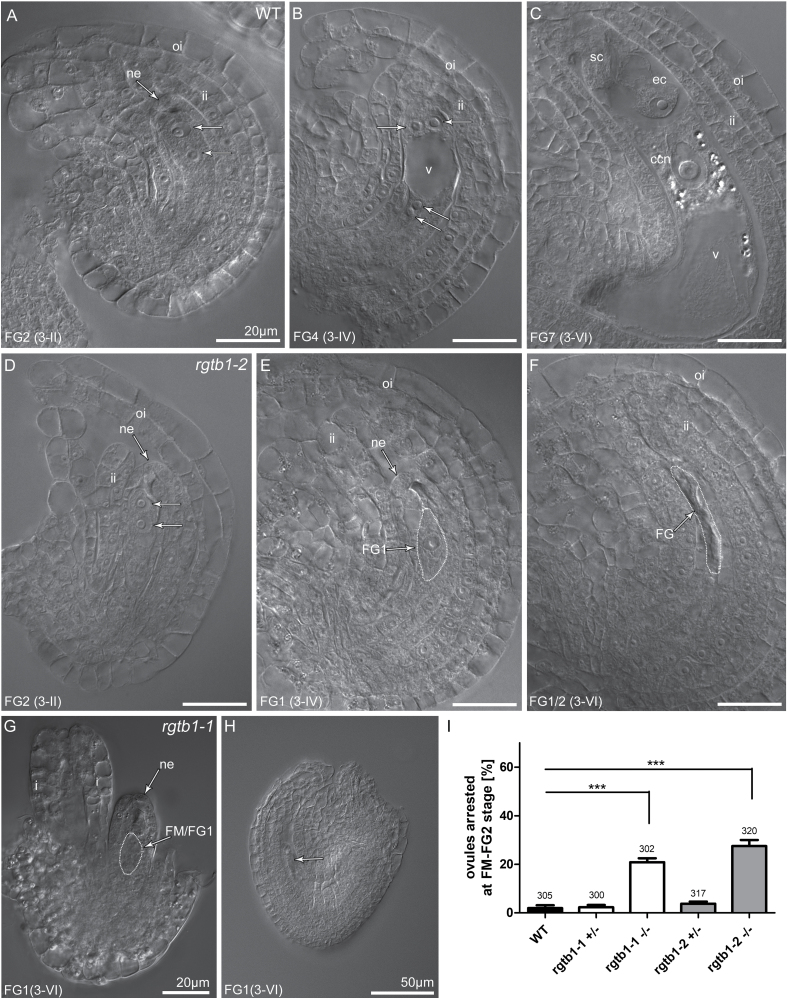
Fig. 2.
The rgtb1 mutation affects ovule and female gametophyte (FG) development. Stages of ovule development in WT (A–C), rgtb1-1 (G and H), and rgtb1-2 (D–F) ovules from flowers at developmental stage 3-I to 3-VI (according to Schneitz et al., 1995; Christensen et al., 1997). (A–C) WT plants; stages of FG development correlate with ovule development. Starting from the 3-I stage (corresponding to the FG2 stage of the ovule in the WT), a developmental arrest is observed in a large portion of rgtb1 ovules at the FM or FG1 stage. Normal development of ovules at the 3-II/FG2 flower stage (A versus D), developmental arrest of the FG in rgtb1 at the 3-IV/FG4 flower stage (B versus E), and the 3-VI/FG6 flower stage (C versus F–H) with normal (E, F, H) or (D, G) abnormal development of integuments. (I) Fraction of ovules arrested at the FM/FG2 stage of gametogenesis (%). In each case, >300 ovules were counted, while the exact number is given above the corresponding bar. Bars represent the mean ±SEM. Data were compared with unpaired Student t-test; ***indicates a P-value <0.001. (A–H) DIC microscopy. Abbreviations: ne, nucellar epidermis; ii, inner integument; oi, outer integument; ec, egg cell; sc, synergid cell; ccn, central cell nucleus; v, central vacuole; FM, functional megaspore; FG, female gametophyte. Nuclei in FGs are marked by arrows (A, B, D). Scale bar=20 μm for all images.