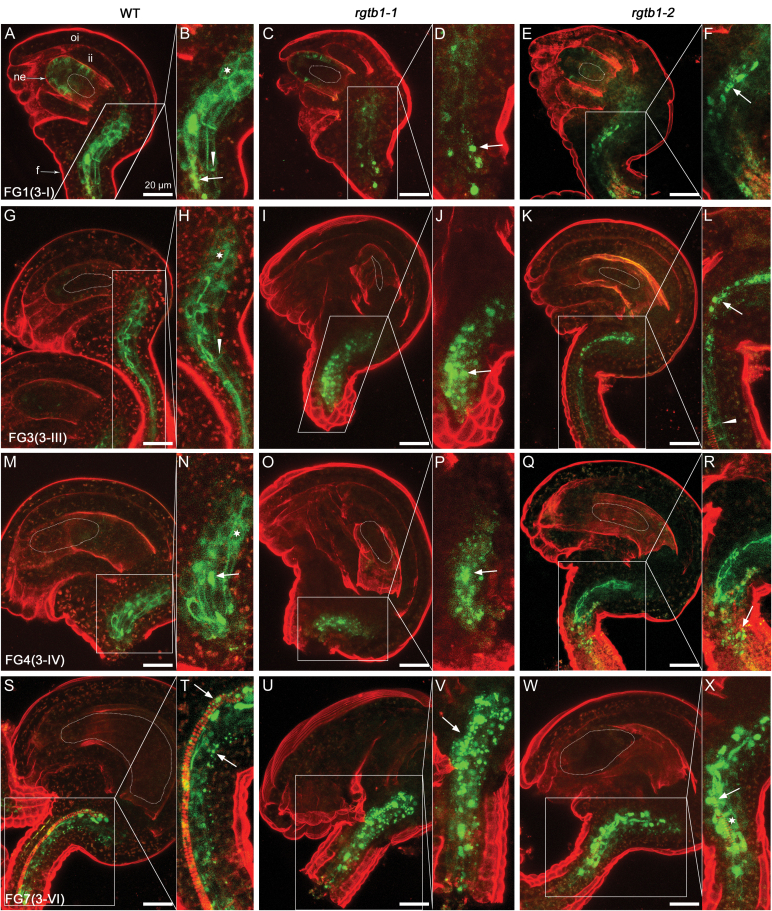
Fig. 4.
PIN1–GFP is internalized in the funiculus provasculature of rgtb1 ovules. pPIN1:PIN1–GFP expression in WT (A, B, G, H, M, N, S, T), rgtb1-1 (C, D, I, J, O, P, U, V), and rgtb1-2 (E, F, K, L,Q, R, W, X) ovules from developmental stage 3-I to 3-VI (according to Schneitz et al., 1995). (A and B) PIN1–GFP is basal polarly localized in provascular cells of the funiculus in the young WT ovules (at the FG1 stage) and with progression of development becomes partly internalized (G and H, at the FG3 stage; M and N, at the FG4 stage) and is internalized in mature ovules (S and T). In a large fraction of rgtb1 ovules, the PIN1–GFP signal is internalized, at least partially, throughout the whole of development, starting from the unicellular stage until mature FG (rgtb1-1 images C, D, I, J, O, P, U, V; rgtb1-2 images E, F, K, L, Q, R, W, X). (A–X) Confocal laser scanning microscopy, PIN1–GFP signal and FM4-64 dye fluorescence. Dotted lines highlight the MMC, FM, or FG, as appropriate for the image. Abbreviations: ne, nucellar epidermis; f, funiculus; ii, inner integument. Basal polar localization of PIN1–GFP is marked by arrowheads, intracellular localization is marked by arrows, and an asterisk marks cells with apolar PIN1–GFP localization. The left narrow image represents a magnification of the area boxed in the right image. Scale bar=20 μm for all images. (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)