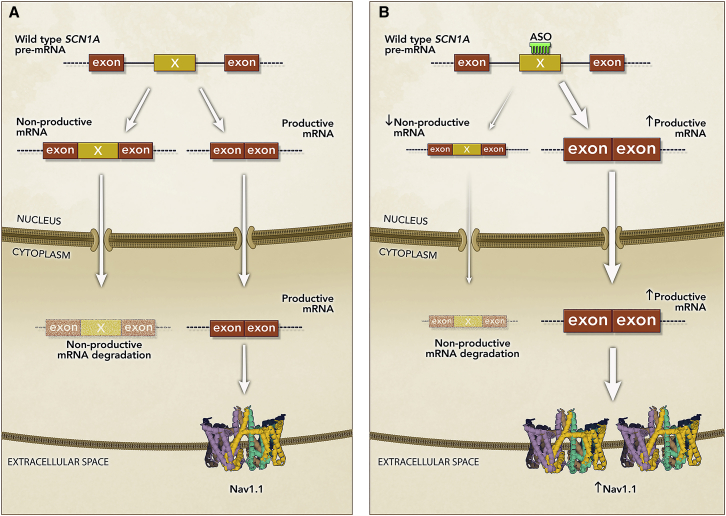
Figure 8.
Mechanism of Action of STK-001, a New Application of Steric-Blocking ASOs
(A) Region of SCN1A wild-type pre-mRNA containing non-productive (non-coding) exon X (yellow rectangle) and flanking coding exons (brown rectangles). SCN1A pre-mRNA is alternatively spliced such that it generates a non-productive mRNA containing the non-productive exon X, which leads to the introduction of a PTC, and a productive mRNA lacking exon X. Upon export to the cytoplasm, the non-productive mRNA is degraded by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and the productive mRNA is translated into wild-type Nav1.1 protein. The pre-mRNA carrying DS mutations undergoes the same alternative splicing processing, but the mutant productive mRNA does not produce a functional protein (not shown in the figure), leading to haploinsufficiency of Nav1.1. (B) STK-001 (ASO) binding to the non-productive exon X of the SCN1A wild-type and mutant (not shown) pre-mRNA and promotes exon X skipping, which leads to a reduction in non-productive mRNA and increased levels of productive mRNA and wild-type Nav1.1 protein to near normal levels. STK-001 leverages the wild-type gene copy to compensate for the loss-of-function mutant alleles in DS patients.