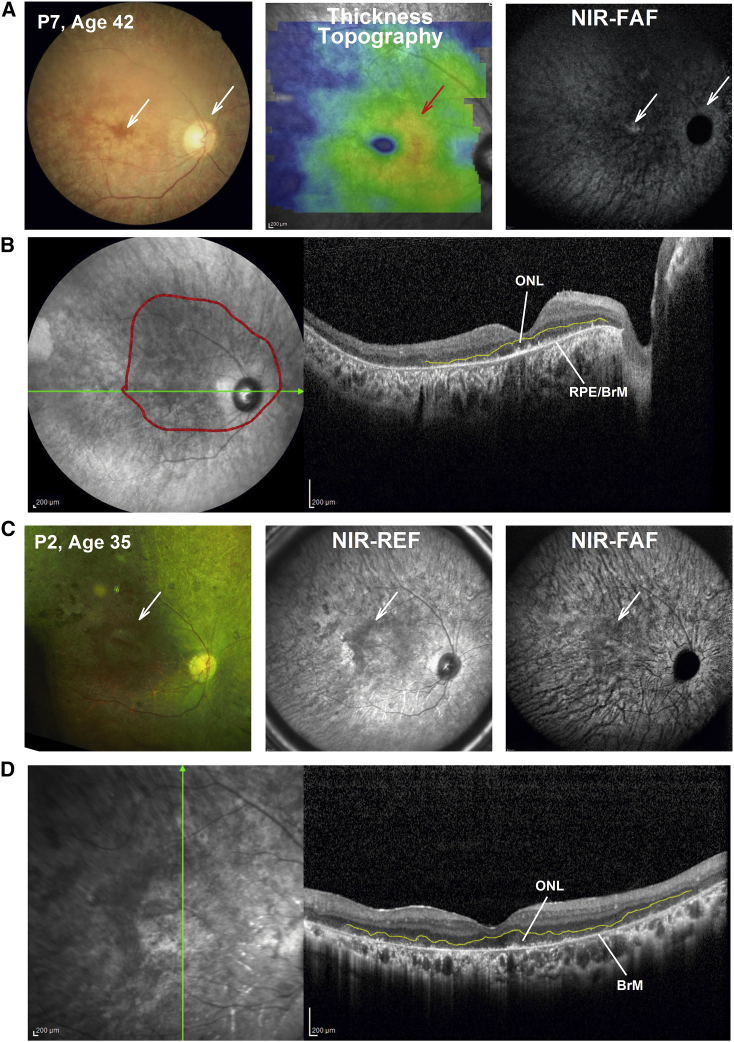
Figure 5.
Structural Details by Multimodal Retinal Imaging in Late-Stage RPE65-IRD
(A) Fundus photography: total retinal thickness topography and NIR-FAF in a patient with severe disease. White arrows points to areas of detectable RPE melanin by fundus photography (left panel) and NIR-FAF (right panel) near the foveal center and in peripapillary retina. As in Figure 4, a red arrow points to an area of increased overall retinal thickness that does not match the gradual, even decline in ONL thickness, symmetrical on either side of the fovea. (B) 16-mm-long horizontal SD-OCT cross-section through the fovea in the same patient. Red line overlaid on the NIR-REF image delineates region with detectable, albeit severely thin, ONL, as demonstrated on the SD-OCT cross-section by outlining the outer plexiform layer in yellow. The RPE/BrM is clearly detectable on the SD-OCT scan, and there are spotty signals above the apical RPE/BrM that may correspond with the abnormal photoreceptor outer segment or its remnants. (C) Fundus photography: NIR-REF and NIR-FAF in a patient with severe disease. White arrows point to areas of relatively better coloration in the parafoveal retina (left panel) possibly reflecting surviving RPE, which corresponds to a darker region on NIR-REF. There is virtually no RPE melanin autofluorescence detectable on the non-normalized NIR-FAF (right panel). The area of better coloration on the color fundus image corresponds with a darker image on the NIR-REF and NIR-FAF image suggesting detectable photoreceptors and demelanized RPE overlaying the background choroidal autofluorescence signals that are crisscrossed by large dark choroidal vessels (right panel). (D) 9-mm-long vertical SD-OCT cross-section through the fovea in the same patient. A severely thin ONL, outlined by the outer plexiform layer (in yellow), overlies a thin RPE/BrM signal that likely corresponds to a severely abnormal RPE or bare BrM devoid of overlying RPE. A severely abnormal to non-detectable RPE, even if photoreceptors are identifiable, may be considered an additional contraindication for AAV2.RPE65 augmentation treatment in RPE65-IRD.