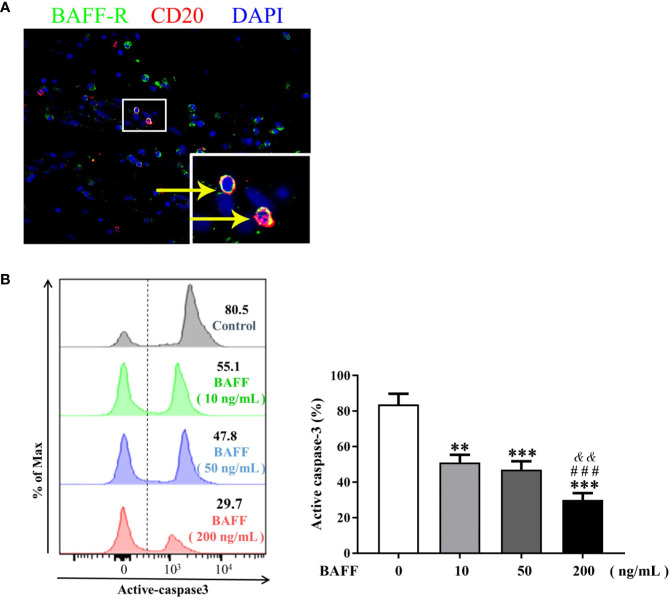
Figure 3.
BAFF treatment rescues nasal polyps (NP) B cells from apoptosis. (A) Double immunofluorescence staining of NP tissues shows BAFF-R expression on CD20+ B cells. Original magnification × 400. Inset shows a higher magnification of the outlined area, and arrows denote positive cells. (B) B cells isolated from NP tissues were treated with 10, 50, and 200 ng/ml BAFF for 48 h. The frequencies of active caspase-3+ B cells in CD19+ B cells were detected by flow cytometry (n = 8). The representative flow plots are shown. BAFF, B cell-activating factor; BAFF-R, B cell-activating factor receptor. ** indicates P < 0.01 vs. control (without BAFF treatment); *** indicates P < 0.001 vs. control (without BAFF treatment); ### indicates P < 0.001 vs. 10 ng/ml BAFF-treated group; && indicates P < 0.01 vs. 50 ng/ml BAFF-treated group.