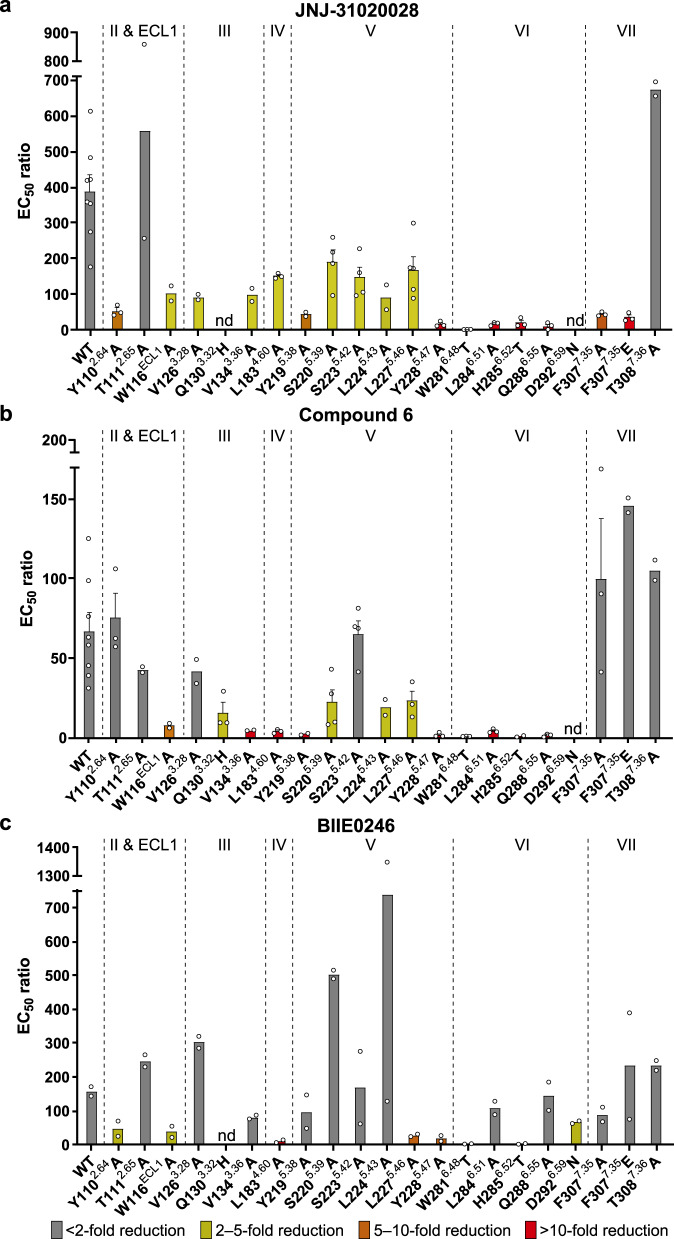
Fig. 3. NPY-induced IP accumulation inhibited by antagonists.
a JNJ-31020028. b Compound 6. c BIIE0246. Bars represent EC50 ratios of the mutated receptors compared to the EC50 ratio of the wild-type Y2R using 1 μM concentration of the respective antagonist. The EC50 ratio refers to the shift between the NPY and NPY + 1 μM antagonist curve (EC50(NPY + antagonist)/EC50(NPY)) and characterizes the antagonistic effect on the wild-type receptor or receptor mutants. By comparison of EC50 ratios between wild-type and mutant receptors, influences of all tested residues on antagonistic activity were determined. A higher ratio indicates higher antagonistic activity. A reduced EC50 ratio of mutant compared to the wild-type receptor was interpreted as important for the respective antagonist. At least two independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Where more than two experiments were performed, data are displayed as mean ± SEM (bars) with individual data points shown (dots). Where two experiments were performed, data are displayed as mean (bars) with individual data points shown (dots). Bars are colored based on the extent of effect (gray, <2-fold reduction of EC50 ratio; yellow, 2–5-fold reduction of EC50 ratio; orange, 5–10-fold reduction of EC50 ratio; red, >10-fold reduction of EC50 ratio). nd, not determined. See Supplementary Table 2 for detailed statistical evaluation. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.