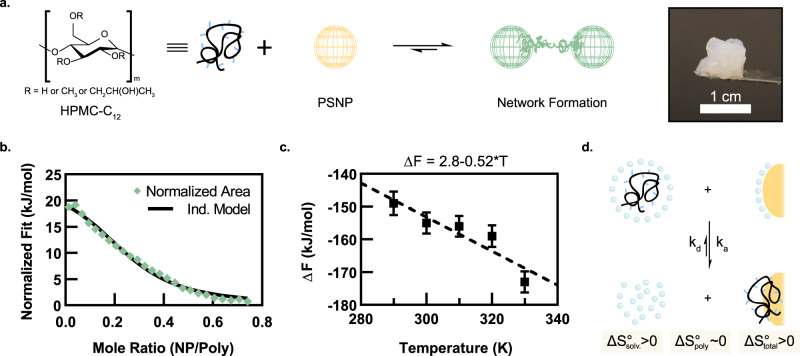
Fig. 2. Polymer–nanoparticle (PNP) hydrogels exploiting entropy-driven interactions.
a Schematic of physical crosslinking between dodecyl-modified hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC-C12) and polystyrene nanoparticles (PSNPs; DH = 57 nm). The photograph shows the opaque hydrogel formed upon mixing of the polymer and nanoparticle constituents. b Normalized integrated heats of an incremental titration of PSNPs into a solution of HPMC-C12 during an isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) experiment. c Adsorption free energy changes calculated from a simulated HPMC-C12 chain pulled off a complementary PSNP surface. Data shown as mean ± standard deviation. d Schematic illustrating the binding of a polymer chain onto a nanoparticle surface and the corresponding entropy changes of each component. PNP interactions form when the entropy change is large and positive, regardless of whether these interactions are endothermic or exothermic.