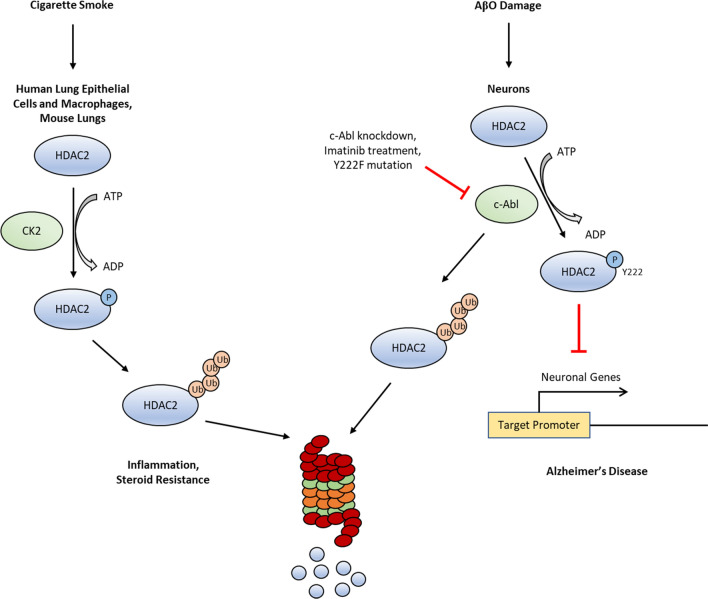
Fig. 3.
Phosphorylation of HDAC2 influences its stability. Phosphorylation of HDAC2 can have different effects on its stability depending on the cellular context. HDAC2 phosphorylation by CK2 in lung epithelial cells, macrophages, and mouse lungs following exposure to cigarette smoke leads to its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Loss of HDAC2 through this mechanism is proposed to play a role in inflammation and steroid resistance associated with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [29]. In neurons, loss of HDAC2 phosphorylation at Y222 leads to the proteasomal degradation of HDAC2, releasing its repression of the transcription of neuronal genes that otherwise occurs in Alzheimer’s disease [68]. P phosphate, Ub ubiquitin