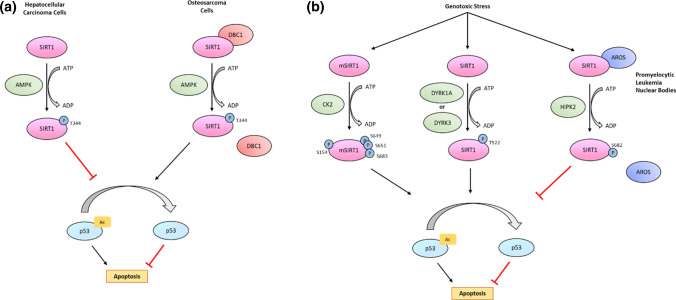
Fig. 4.
Relationship between SIRT1 phosphorylation and p53-mediated apoptosis. a Phosphorylation of SIRT1 at T344 by AMPK can have opposing effects on p53 acetylation, depending on the cellular context. SIRT1 phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells inhibits its activity in deacetylating p53 and promotes apoptosis [48]. In contrast, its phosphorylation in osteosarcoma cells disrupts its interaction with its inhibitor, DBC1, allowing SIRT1 to deacetylate p53 and inhibit apoptosis [84]. b Genotoxic stress leads to the phosphorylation of SIRT1 at different sites by several kinases, including CK2, DYRK1A, DYRK3, and HIPK2, which influences the ability of SIRT1 to deacetylate p53. CK2- and DYRK-mediated phosphorylation of SIRT1 support its ability to deacetylate p53 and inhibit apoptosis [45, 46]. In contrast, SIRT1 phosphorylation by HIPK2 disrupts its interaction with its activator, AROS, which inhibits the deacetylation of p53 and leads to apoptosis [47]. P phosphate, Ac acetyl group