Fig.1 |. Cryo-EM structure of the Sth1-Arp7-Arp9-Rtt102 RSC subcomplex (RSCSAR) bound to a nucleosome.
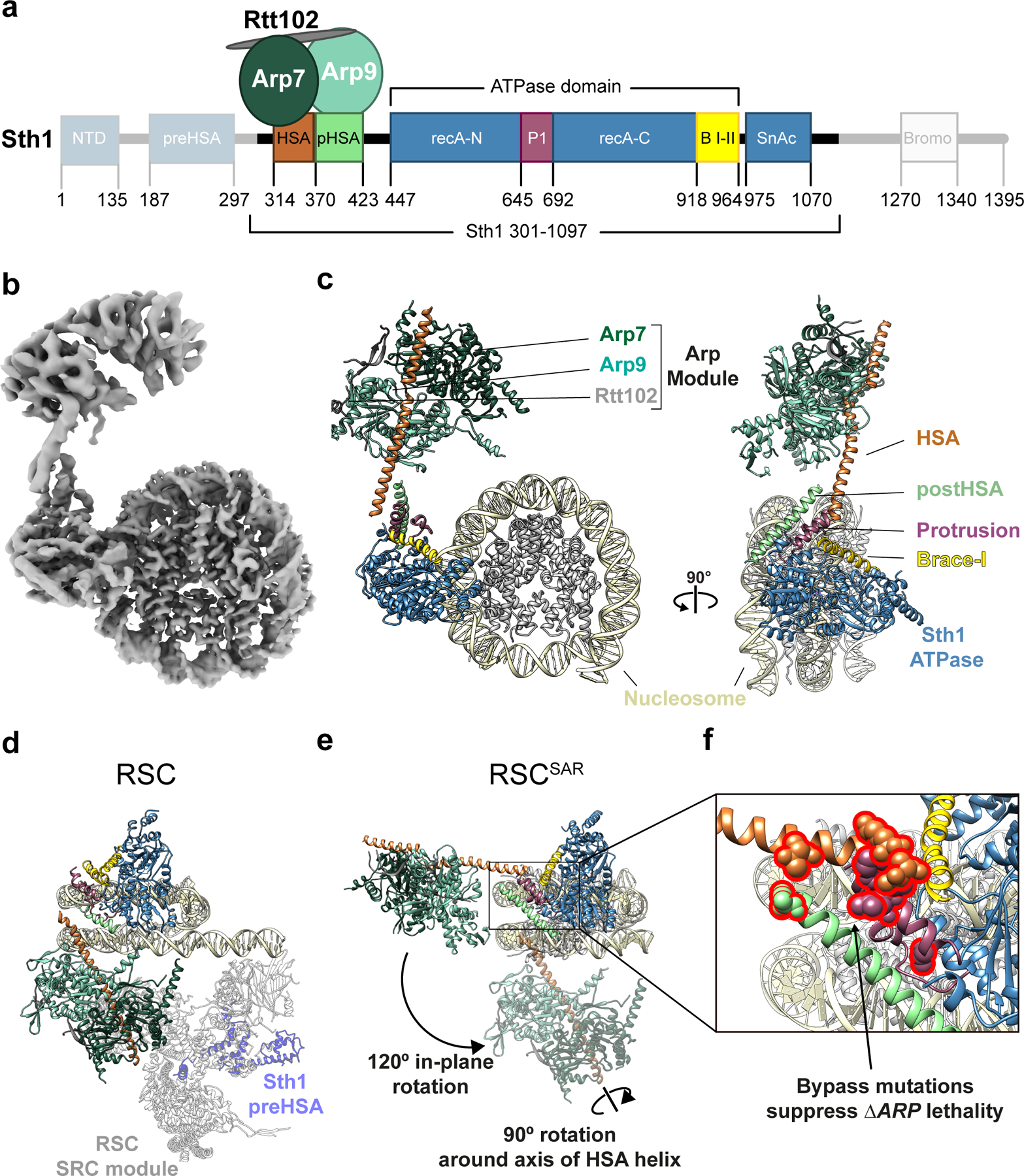
a, Schematic representation of RSCSAR, with Sth1 domains and their boundaries indicated. The same color scheme is used in all figures. b, 3.9 Å Cryo-EM map of RSCSAR bound to a nucleosome. c, Molecular model of the RSCSAR:nucleosome complex. d, e, Large rotations relate the position of the ARP module in RSCSAR and RSC. d, Structure of a RSC:nucleosome complex (PDB 6KW3) with the portion corresponding to RSCSAR shown with the same colors introduced above. The N-terminal portion of Sth1 preceding the HSA, which is absent in the Sth1 construct used in RSCSAR, is shown in dim purple. The Substrate Recognition Complex (SRC) of RSC is shown in grey. e, RSCSAR is shown with the nucleosome and Sth1 in the same orientation as that in (d). The position occupied by the ARP module in RSC (d) is shown in dim colors. The movements required to convert the ARP module from its position in RSCSAR to that in RSC—a 120° in-plane rotation and a 90° rotation about the HSA helix—are indicated. f, Close up of the regulatory hub located at the base of the HSA helix, consisting of the C-terminal end of the HSA helix, the postHSA and P1.
