Figure 1:
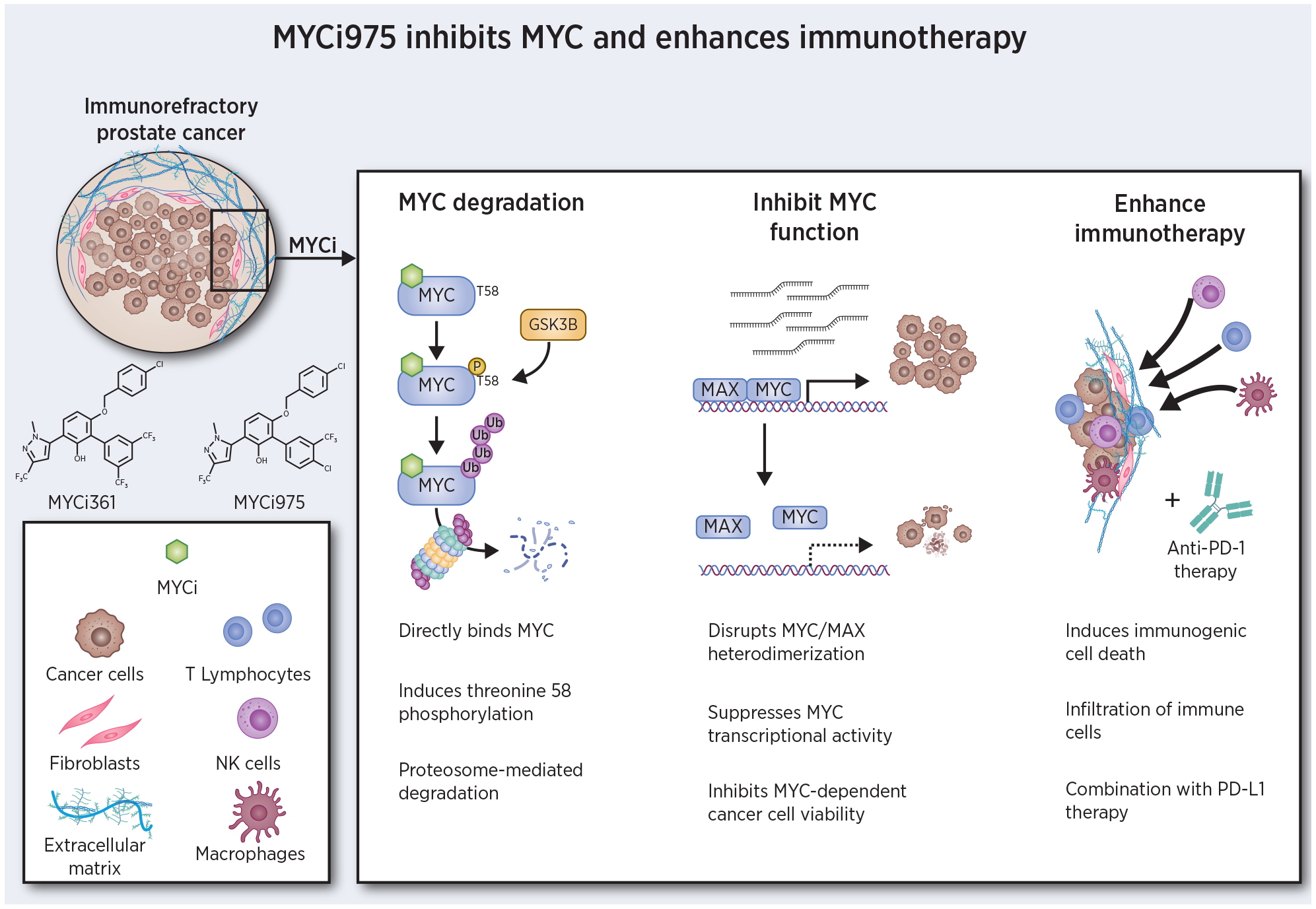
Mechanism of MYCi efficacy. MYCi directly binds to MYC, induces phosphorylation of threonine 58 leading to MYC degradation. MYCi inhibits MYC/MAX heterodimerization, blocking MYC-dependent transcription and proliferation. Following MYCi treatment, the tumor microenvironment is altered by infiltration of diverse immune effector cells and increased PD-L1 expression. Combination of MYCi with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy results in improved efficacy.
