Fig. 4 |. Interactions between RSP3 and radial spoke proteins.
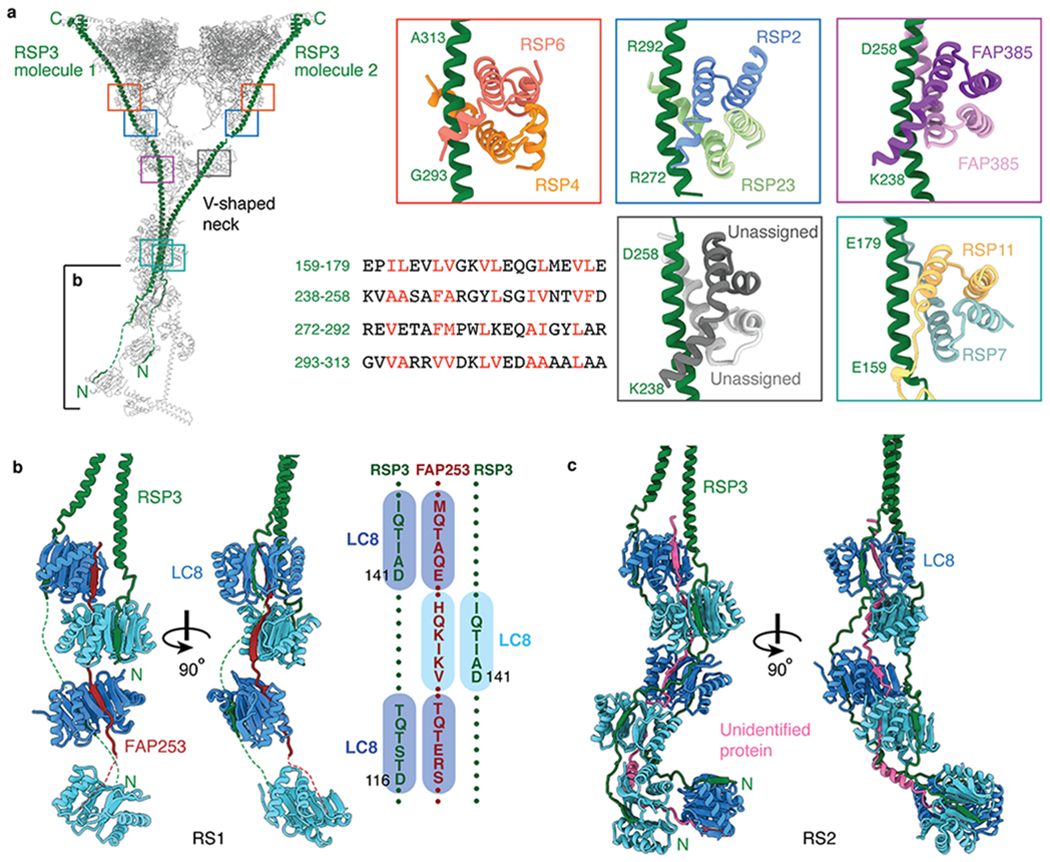
a, Left, atomic model of RS1 with its two molecules of RSP3 colored green. Colored boxes indicate the binding sites on RSP3 of five different dimers. The partially boxed proximal region of the stalk is shown in detail in panel b. Right, atomic models of the interactions between RSP3 and different dimers. The sequence alignment shows amphipathic helices of RSP3 with hydrophobic residues recognized by the various dimers colored red. The four-helix bundle of RSP7/RSP11 belongs to the RIIa dimerization/docking domain and the four-helix bundles of RSP4/RSP6, RSP2/RSP23, RSP385/RSP385 and the unassigned dimer belong to Dpy-30 domain (which has an additional helix at the N-terminus compared with RIIa dimerization/docking domain). b, Left, orthogonal views of the interactions of RSP3 and FAP253 with the LC8 homodimers in RS1. Other subunits have been omitted for clarity. Right, a schematic showing the resolved LC8-binding motifs of FAP253 and RSP3. c, Orthogonal views of the interactions between RSP3 and the LC8 homodimers in RS2. An unassigned protein (pink) also interacts with the β-edges of LC8. Other subunits have been omitted for clarity.
