Fig. 5 |. IDA subforms a and c dock onto the bases of radial spokes.
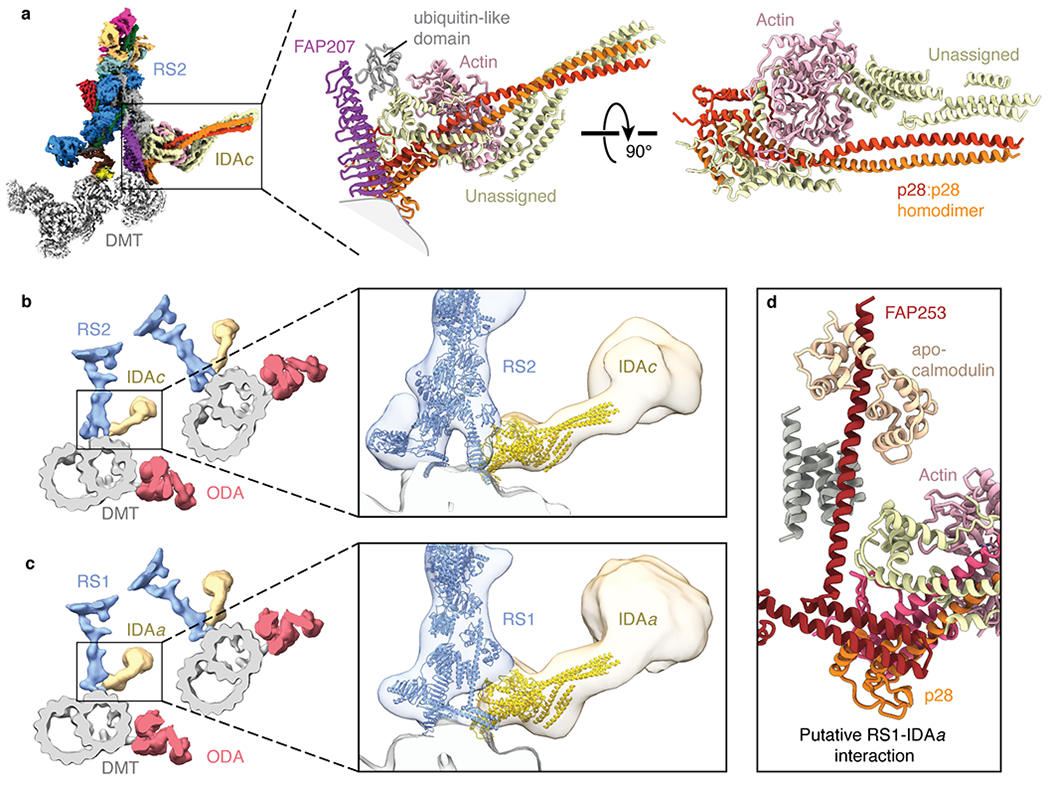
a, Left, composite map showing the densities for the base of radial spoke 2 (RS2), inner dynein arm subform c (IDAc), and the doublet microtubule (DMT). The maps of RS2 and IDAc are colored by subunit. Right, atomic model of IDAc showing the interaction with FAP207 and an unidentified ubiquitin-like domain of RS2. The unassigned helices of IDAc may correspond to the tail of the dynein heavy chain. b, Left, slice through the subtomogram average of the Chlamydomonas axoneme (EMD-6872) with RS2 colored blue, IDAc colored yellow, outer dynein arm (ODA) colored red, and the DMT colored gray. Zoomed-in view showing the models of RS2 and IDAc (colored blue and yellow, respectively) docking into the subtomogram average. c, Left, slice through the subtomogram average of the Chlamydomonas axoneme (EMD-6872) with radial spoke 1 (RS1) colored blue, inner dynein arm subform a (IDAa) colored yellow, ODA colored red, and the DMT colored gray. Zoomed-in view showing the atomic models of RS1 and IDAc (colored blue and yellow, respectively) docking into the subtomogram average. The putative interface between IDAa and RS1 is distinct from the interface between RS2 and IDAc. d, Details of the expected interface between RS1 and IDAa based on docking the model of IDAc into the subtomogram average map of IDAa (EMD-6872).
