Fig. 3.
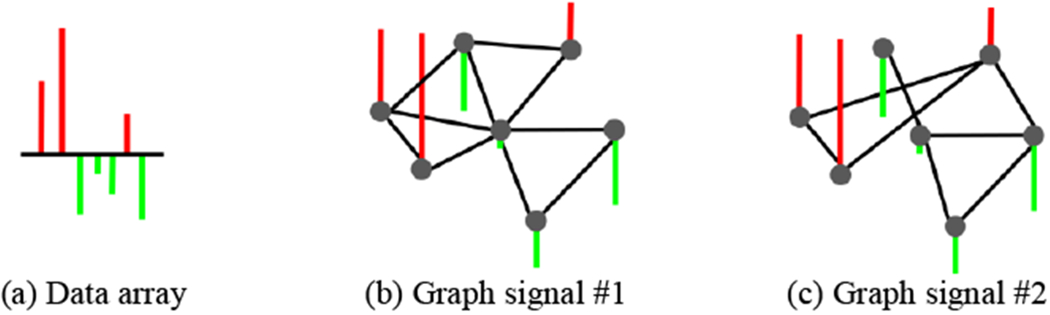
A data array (a) can potentially reside on different graphs and form different graph signals (b)-(c). However, only one leads to the smooth graph signal where the strongly connected nodes have similar values. Hence, graph signal in (b) is more reasonable than graph signal in (c) after inspecting the values for each pair of connected nodes, where the red and green denote for positive and negative degrees.
