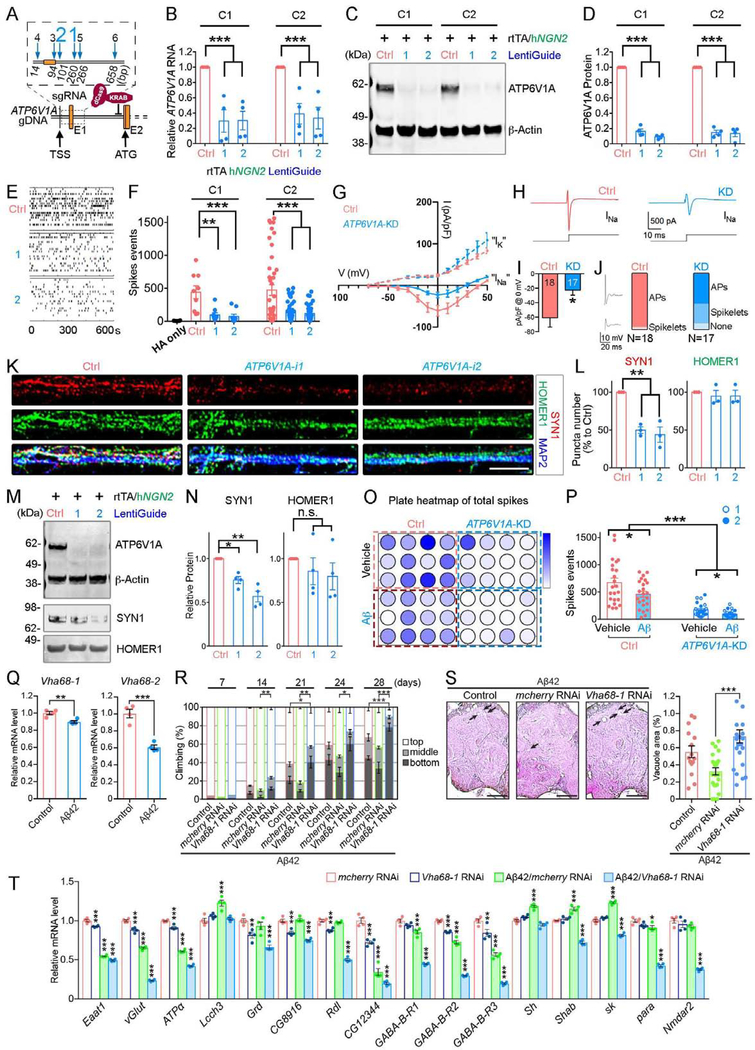
Fig. 4. Repression of ATP6V1A leads to neuronal malfunction in human NGN2-neurons and Aβ42 transgenic flies.
A, ATP6V1A gene editing by the CRISPR/dCas9-KRAB system. 6 different gRNAs are designed for targeting the ATP6V1A promoter. TSS: transcription start site. ATG translation initiation codon is in exon 2. B, qRT-PCR analysis (n = 4) confirms the decreased ATP6V1A RNA by gRNA candidates 1 & 2 (i1 and i2) in 2 independent cell lines of iNs (i.e., C1 and C2). C-D, Representative WB and quantitative analysis (n = 4) of ATP6V1A protein level in iNs. β-Actin is a loading control. E-F, Representative raster plots of spike events over 10 min and analysis (n = 6~45 wells) of D21 iNs. G, Current-voltage (I-V) plot for inward sodium (INa) and outward potassium (IK) currents. Current density (pA/pF) is shown. Holding potential was −80 mV. H, Representative examples of putative inward voltage-gated sodium current at 0 mV. I, Bar plot shows mean inward sodium current densities at 0 mV for ATP6V1A KD (n=17) and control neurons (n=18), (p = 0.015). J, Box plots show the fraction of neurons that displayed a full action potential (AP), spikelets, or no events with a current injection step (0.1 nA) positive to the threshold for control and KD neurons. Inset shows representative examples of AP & spikelet. K, Representative confocal images of synaptic proteins (SYN1, red; HOMER1, green) and pan-neuronal marker MAP2 (blue). Bar, 20 μm. L, Analysis of SYN1 and HOMER1-immunoreactive puncta numbers (n = 3). M-N, Representative WB and quantitative analysis (n = 4) of SYN1 and HOMER1 levels. O-P, Multi-electrode array after exposure to 5 μM Aβ at 24 hours. O, Plate map of total spike events; P, Analysis of spike events (n = 12 wells). Q, mRNA levels of Vha68–1 and Vha68–2 were decreased in the Aβ42 fly heads (n = 4). R, Vha68–1 KD in neurons exacerbated locomotor deficits caused by Aβ42 as revealed by climbing assay. n = 5 except for 7-day (n = 2). S, Neuronal KD of Vha68–1 significantly worsened neurodegeneration in Aβ42 fly brains. Representative images show the central neuropil of 33-day-old fly brains. Scale bars: 50 μm. Percentages of vacuole areas (indicated by arrows) were analyzed. n = 12–24 hemispheres. T, mRNA levels of genes related to synapse biology were significantly reduced in Aβ42-expressing flies with neuronal KD of ATP6V1A/Vha68–1 (n = 4). See also Fig. S16–21. (See Fig. 3 for statistical test and P value annotations).