Figure 6.
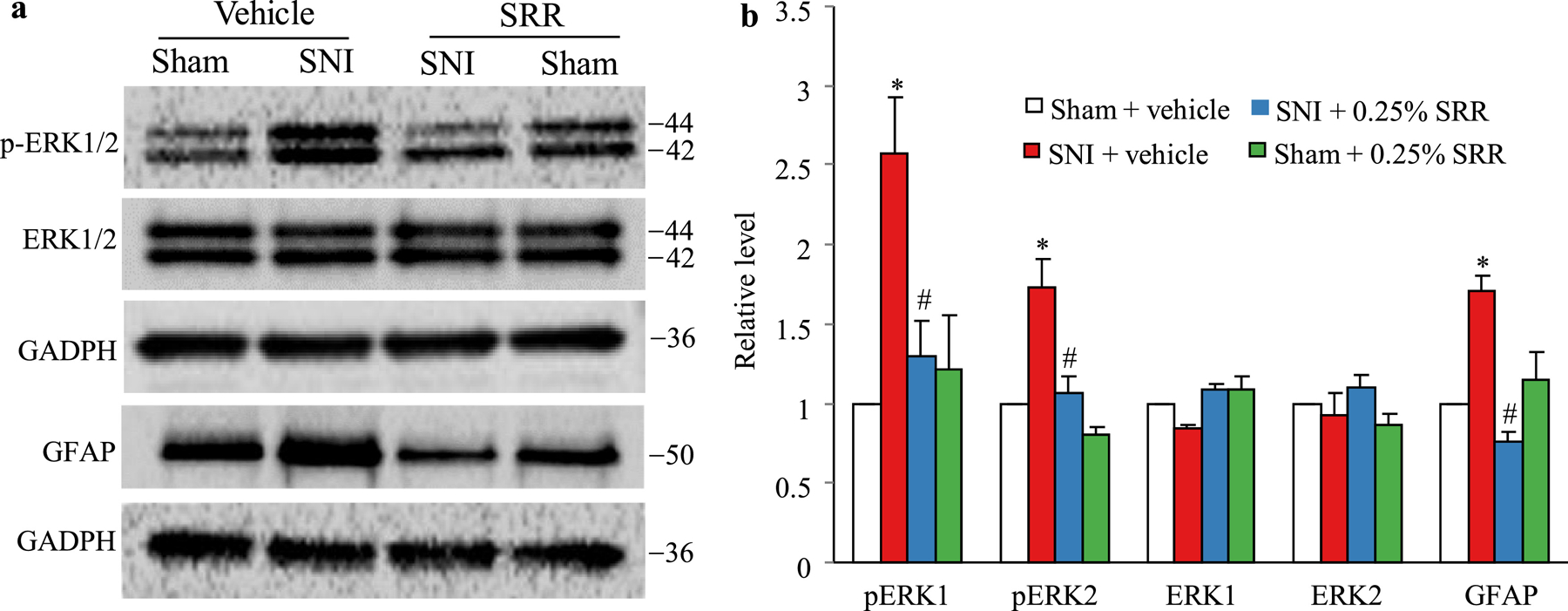
Effect of peri-sciatic nerve injection of 0.25% SRR or vehicle on spare nerve injury (SNI)-induced increases in the levels of phosphorylation of extracellular signal–regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the ipsilateral L4/5 spinal cord on day 12 post-SNI or sham surgery (that is, 5 d after SRR or vehicle injection). Representative Western blots (a) and a summary of densitometric analysis (b) are shown. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M of 3 biological repeats (6 rats) per group. One-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by post hoc Tukey test. *P < 0.05 comparison between the vehicle-treated SNI group and the corresponding vehicle-treated sham group. #P < 0.05 comparison between the 0.25% SRR-treated SNI group and the corresponding vehicle-treated SNI group.
