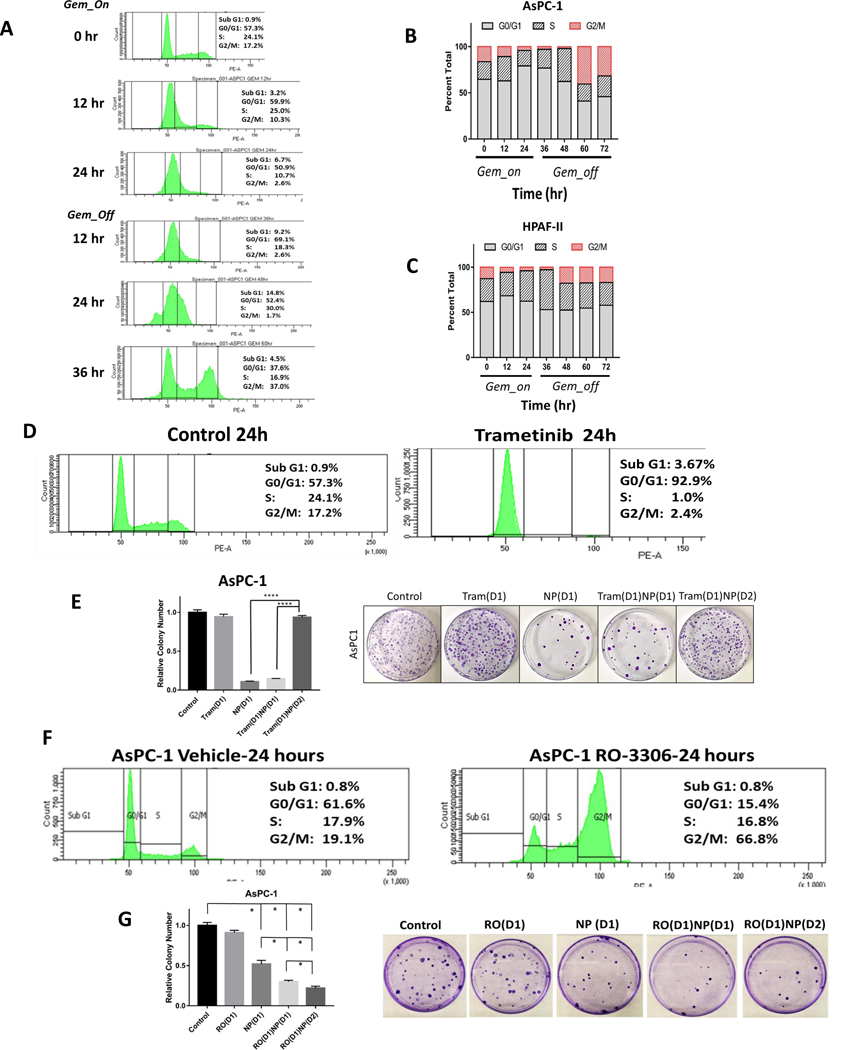
Figure 5.
Gemcitabine treatment results in cell cycle synchronization into G2/M phase after gemcitabine removal. A. Cell cycle analysis of AsPC-1 cells by propidium iodide staining following gemcitabine treatment (50 nM) for 24 hours and following removal of gemcitabine at 60 hours (36 hours after gemcitabine removal). B. Representative bar graphs of cell cycle percentages at 12 hour time points during gemcitabine treatment for AsPC-1 and C) HPAF-II cells shows increase of G2/M proportion after 24–36 hours after gemcitabine removal (at time 48–60 hr). D. Trametinib treatment for 24 hours arrests AsPC-1 cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. E. Pre-treatment of AsPC-1 cells with trametinib for 24 hours followed by 24 hour NP (1 nM) treatment [Tram(D1)NP(D2)] results in abrogation of colony forming inhibition observed with the treatment using NP alone or trametinib and NP treatment on the same day [Tram(D1)NP(D1)]. F. RO-3306 (10 μM) treatment for 24 hours arrests cells in the G2/GM phase of the cell cycle after staining with propidium iodide. G. Pre-treatment of AsPC-1 cells with RO-3306 for 24 hours, followed by NP treatment [RO(D1)NP(D2)] for 24 hours results in increased cell colony forming inhibition compared with RO-3306 alone [RO(D1)], NP alone [NP(D1)], or RO-3306 and NP treatment on the same day [RO(D1)NP(D1)]. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p<0.0001.