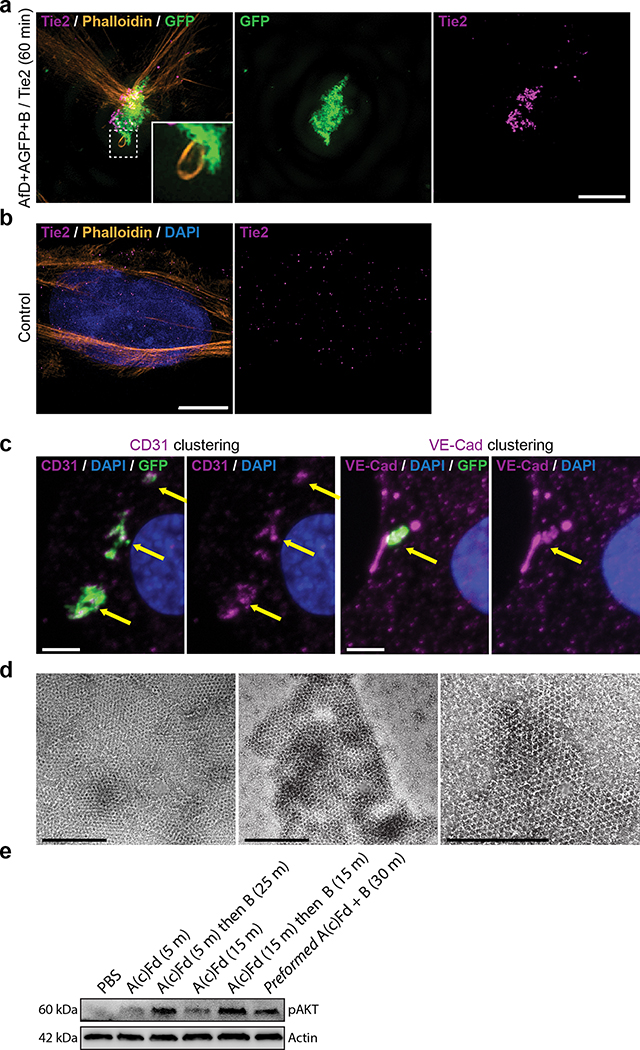
Extended Data Figure 7. Tie2 receptor clustering and CD31/VE-Cad recruitment.
(a,b) Clustering of Tie2 receptors. Imaging of cells incubated for 60min with GFP-positive arrays functionalized with the F domain of the angiogenesis promoting factor Ang1 (a,c), or not (b), then fixed and processed for immunofluorescence with Tie2 antibodies (a,b), CD31 (c, left two panels) or VE-CAD (c, right two panels) antibodies. Note that Tie2 signal is dramatically reorganized and colocalizes with the array (compare a and b). (c) Recruitment of CD31 and VE-Cad under the F domain array (arrows), together with the extensive Actin remodeling (Fig. 3f and inset to a left panel), suggests that the structure induced by the array is a precursor to adherens junction. (d) Negative stain TEM validation of arrays formation using pre-functionalized components AscstfD+BcGFP (A component with a genetically fused spyCatcher peptide fused to spyTag-fDomain (see Table S10 for sequences), and cyclic B component with genetically fused GFP). (e) Assembly of Tie2 cluster via on-cell assembly of arrays is as potent at inducing AKT signalling as preformed arrays. The A(c)fD alone elicits much less AKT phosphorylation alone than when assembled into arrays by the B subunits on cells. Assembly here is done sequentially as in Figure 4 by first incubating with A(c)fD followed by extensive washing of unbound A(c)fD, then by adding the B subunit. As a reference, cells were treated with preformed A(c)Fd+B arrays. Induction of phospho AKT is similar between A(c)fD+B arrays assembled on cells or pre assembled. Scale bars: (a,b,c) 2.5 μm, (d) 500nm.