Fig. 1.
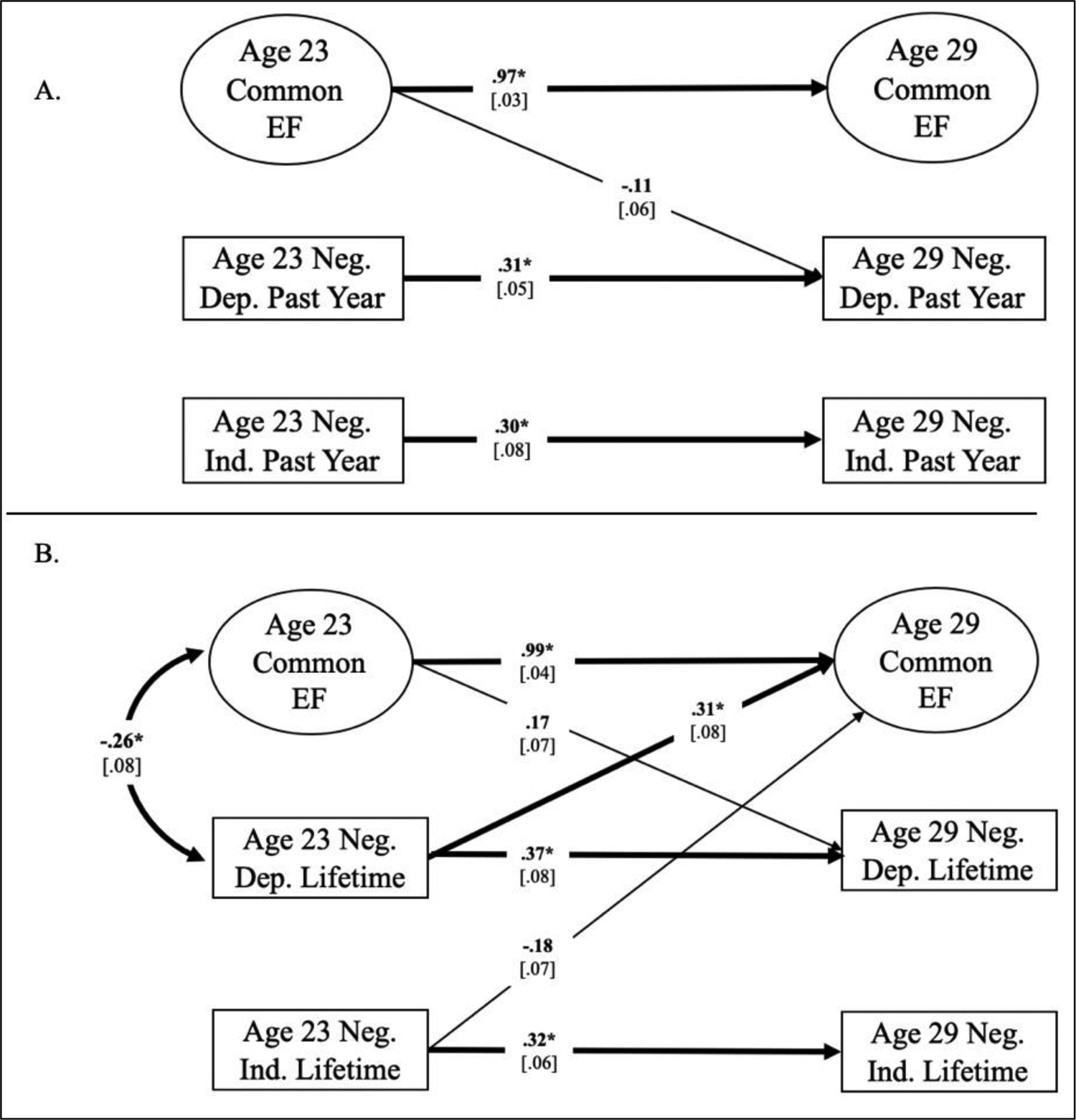
Phenotypic cross-lagged panel models of stress variables and Common Executive Function (Common EF). Panel A shows a model with Common EF and past year stress variables; panel B shows a model with Common EF and lifetime stress variables. Numbers on cross paths are standardized regression coefficients and numbers on double headed arrows are correlation estimates (standard errors are in brackets). For simplicity, only parameters that were at least nominally significant are pictured, the EF measurement model is not shown and Updating-specific and Shifting-specific EF latent factors are not pictured, although they were included in the model. The full models are presented in Figure S4 in the Supplemental Materials. Also not shown are the non-significant regression paths from age 23 EFs to both age 29 stress variables, regression paths from both age 23 stress variables to age 29 EFs, and correlations between each EF and both stress variables within age 23 and age 29, although these were included in the model; Table SX in the Supplemental Materials presents all non-significant regression and correlation coefficients. Thicker lines and * indicate p< .0083; boldface type and thinner lines indicate p< .05.
