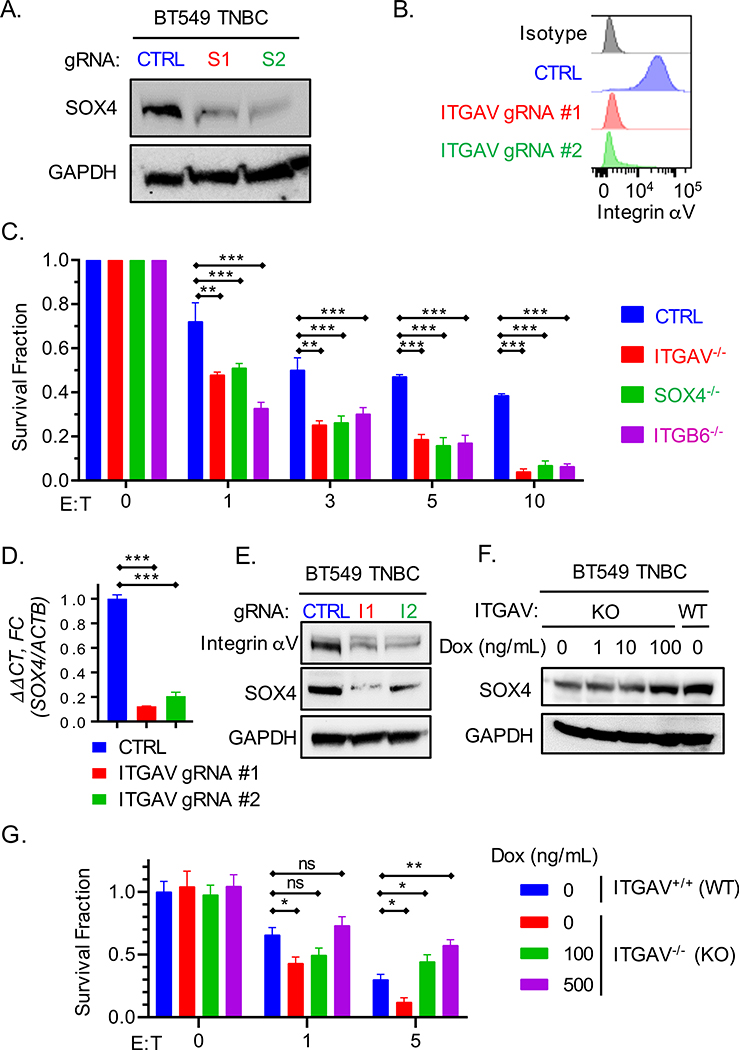
Fig. 1. Inactivation of SOX4 or ITGAV genes sensitizes tumor cells to cytotoxic T cells.
(A) Immunoblot showing SOX4 protein expression by human BT549 TNBC cells edited using two SOX4 gRNAs (S1, S2) or a control gRNA (CTRL). (B) Cell surface expression of integrin αv in BT549 TNBC cells edited with two ITGAV gRNAs (ITGAV gRNA#1 and #2) or a control gRNA (CTRL). (C) T cell cytotoxicity assay with human BT549 TNBC cells edited with SOX4, ITGAV, ITGB6 or control gRNAs. Human T cells expressing a NY-ESO-1 specific TCR were co-cultured for 24 h with tumor cells at the indicated E:T ratios. Data represent the mean of surviving tumor cell fraction after 24 h of co-culture for two independent gRNAs +/− SEM; data are shown relative to condition without T cells (E:T = 0). (D) RT-qPCR analysis of SOX4 mRNA levels in BT549 cells edited with ITGAV or control gRNAs represented as mean ± S.E.M. (E) Immunoblot showing SOX4 protein levels in human BT549 TNBC cells edited with two ITGAV targeting gRNAs (I1, I2) or a control gRNA (CTRL). (F-G) Impact of doxycycline-inducible SOX4 expression in ITGAV KO BT549 tumor cells on resistance to cytotoxic T cells. (F) Immunoblot showing levels of SOX4 and GAPDH proteins in ITGAV+/+ (WT) or ITGAV−/− (KO) BT549 human TNBC cells containing a doxycycline (DOX) inducible SOX4 cDNA construct. Cells were treated with the indicated concentration of doxycycline for 48 h. (G) T cell cytotoxicity assay with ITGAV WT or KO BT549 TNBC cells co-cultured with human NY-ESO-1 specific CD8+ T cells at indicated E:T ratios following pre-treatment with the indicated concentrations of doxycycline for 48 h. Data in (C, D, and G) are representative of at least two independent experiments with technical triplicates and summarized as mean ± S.E.M. Data in [A, B, E, F] were repeated at least three times with consistent results. To determine statistical significance, a two way ANOVA with Dunnett’s [C] or Tukey’s [G] post hoc test or an unpaired Student t-test [D] was used. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05; n.s., not significant. See also Figure S1.