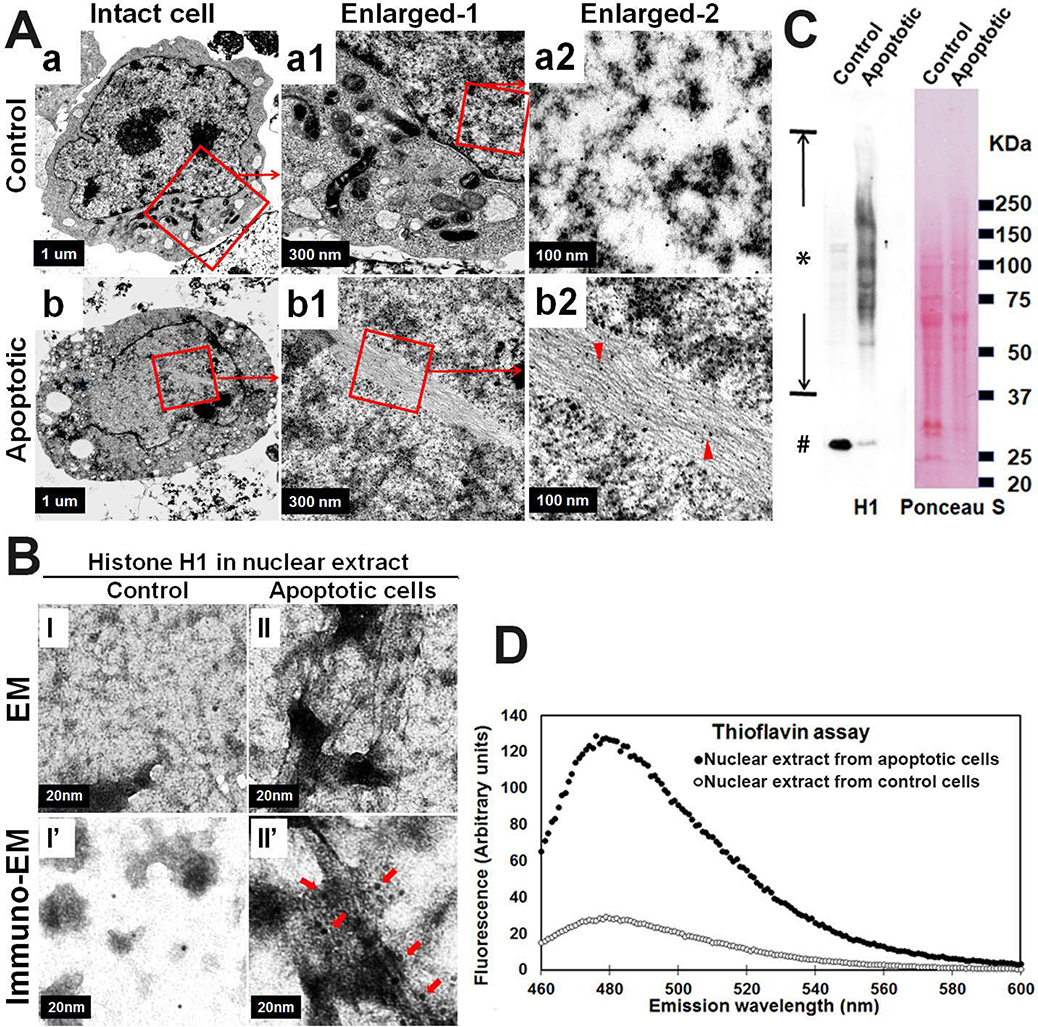
Fig. 2. Nuclear histone amyloid fibrils form in apoptotic neuron cells.
Neuroblastoma cells M17D with αS knockout (M17D/αS-KO) were differentiated for 7 days then subjected to MPTP for 2 days to induce apoptosis. Sibling cells treated by vehicle were used as control. Cells from each group were harvested and divided into 2 fractions. (A) One fraction was processed for immuno-EM, which demonstrated histone H1-immunopositive filamentous structures in nuclei from apoptotic neurons (see “a, a1, a2” & “b, b1, b2”). Arrow heads in (b2) denote histone H1-immunopositive amyloid fibrils in an intact nucleus of an apoptotic cell (organelles are decreased compared with control cells); (B, C &D) The other fraction was used for isolation of nuclei and then generation of nuclear extracts. Nuclear extracts were further divided into three sub-fractions: (B) One sub-fraction was subjected to negative staining EM (I and II) and immuno-EM (I’ and II’) to demonstrate histone H1 immunopositive filamentous structure in nuclear extracts isolated from apoptotic neurons. Arrows in (II’) denote histone H1-immunopositive amyloid fibrils in nuclear extracts isolated from apoptotic neurons; (C) The second sub-fraction from apoptotic neurons was subjected to SDS-PAGE and western blotting to demonstrate a series of histone H1 immunopositive bands, ranging from monomers (denoted by number sign #) to aggregated high molecular weight species (denoted by asterisk sign). Ponceau S staining of the blot was used to confirm that comparable protein was loaded in the two groups; (D) The third sub-fraction was subjected to a Thioflavin T assay to measure the content of beta-sheet (amyloid) in the samples. Primary antibody for detection of histone H1: sc-8030, Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Colloidal Gold Conjugate: GA1003, Boster Bio.