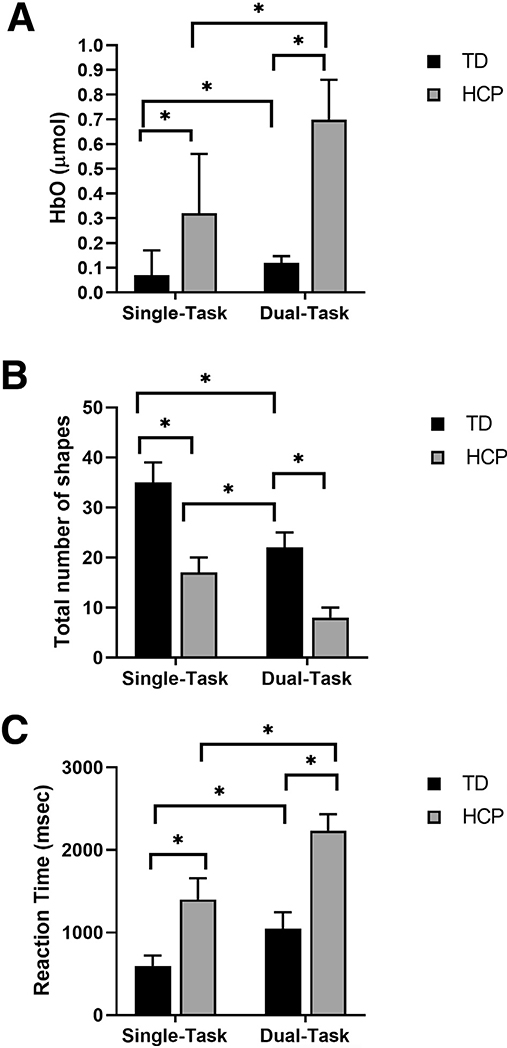
Fig 2.
(A) PFC activation: comparison of the average HbO between TD children (n=12) and children with HCP (n=9) while performing the shape-matching task during single- vs dual-task conditions. Mixed-model ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc analysis shows that the concentration of HbO was highest during dual-task condition followed by single-task condition in children with HCP compared with dual- and single-task conditions in TD children. (B) Total number of shapes matched: comparison of the task performance between TD children (n=12) and children with HCP (n=9) while performing the shape-matching task during single- vs dual-task conditions. Mixed-model ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc analysis shows maximum deterioration of the task performance was observed in dual-task condition followed by single-task condition in children with HCP compared with dual- and single-task conditions in TD children. (C) Reaction time: comparison of RT between TD children (n=12) and children with HCP (n=9) during single- vs. dual-task conditions. Mixed-model ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc analysis shows that the RT was most delayed during dual-task condition followed by single-task condition in children with HCP compared with dual- and single-task conditions in TD children. NOTE. The error bars are standard error of mean. *P≤.01.