Fig. 3 |. Overcoming challenges in eliciting bnAbs and ADE.
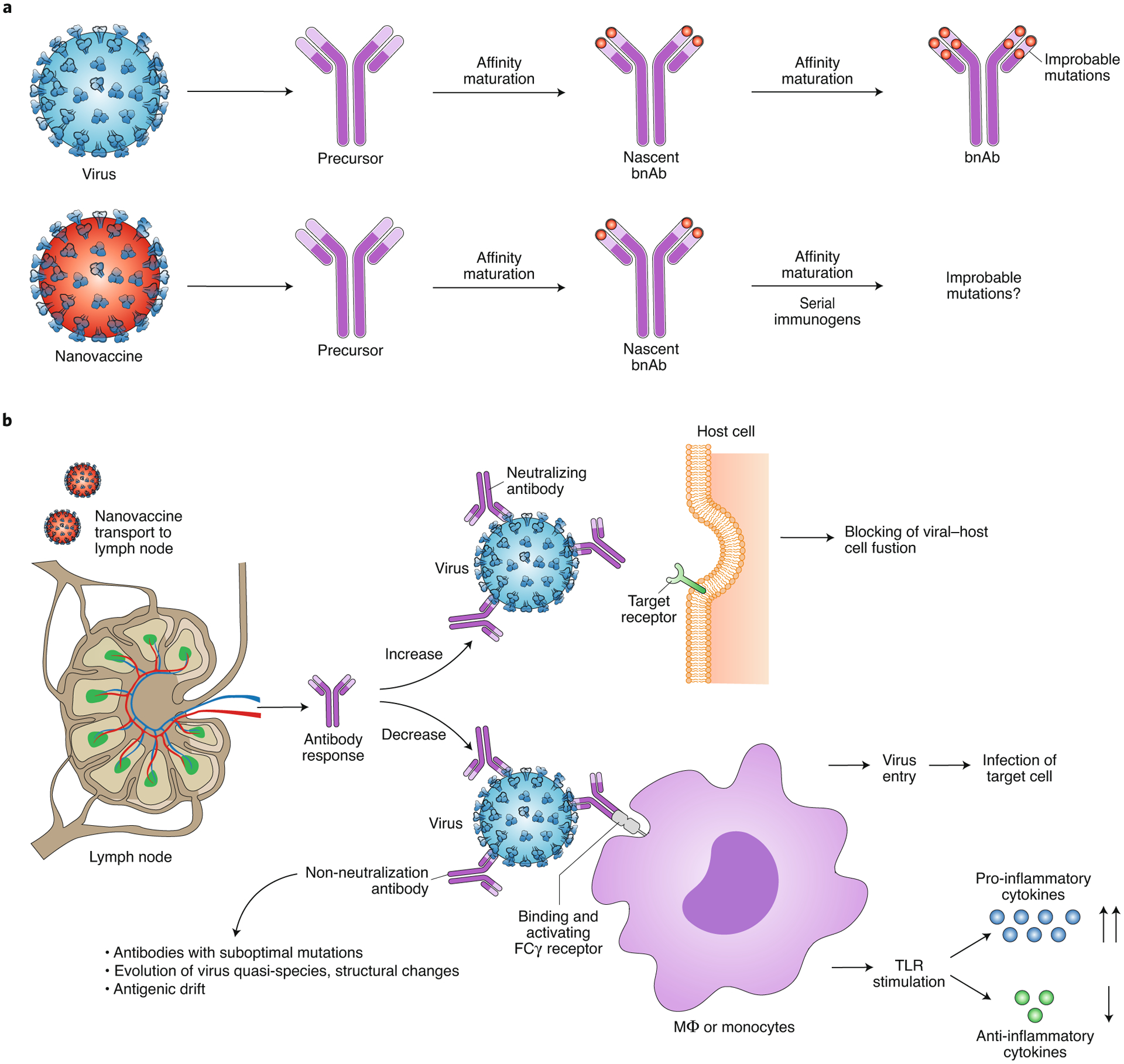
a, bnAbs require complex somatic hypermutations to acquire improbable mutations for neutralizing activity. Conventional vaccines face this somatic hypermutation roadblock and do not typically elicit bnAbs like an infectious response. Immunoengineered nanovaccines can elicit antibodies that exhibit neutralization activity similar to that of intermediate-stage bnAbs. By rationally combining nanoparticles with structurally engineered immunogens followed by serial immunizations, improbable mutations, akin to infection, may be achievable. b, ADE may impose a challenge in nanovaccine design and elicited immune response. Nanovaccines may induce high-quality, mutated, neutralizing antibodies that would bind to targeted proteins on pathogen surface and inhibit host-pathogen interaction. Nanovaccines may reduce production of non-neutralizing antibodies, which can use their Fab domain to attach to pathogens, without neutralizing them he, and their Fc domain to bind to the corresponding receptors on innate immune cells, actually facilitating infection and/or induction of a cytokine storm through the stimulation of TLRs.
