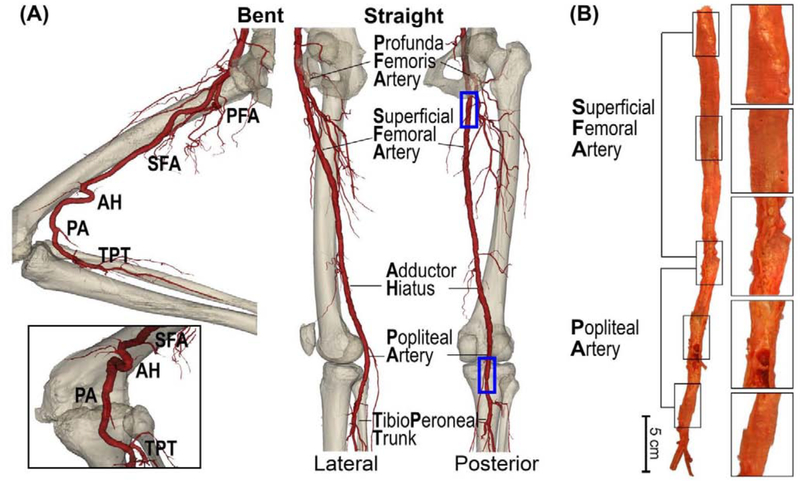
Figure 1:
(A) Anatomy of the femoropopliteal artery (FPA) in the straight (right) and bent (left) limb posture. The FPA is typically divided into the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and the popliteal artery (PA) at the level of the adductor hiatus (AH). The SFA starts at the take off of the profunda femoris artery (PFA) in the upper thigh, and the PA ends at the tibioperoneal trunk (TPT). Note that the artery at the adductor hiatus and behind the knee is experiencing severe deformations during limb flexion. (B) A representative image of the longitudinally-opened 79-year-old male femoropopliteal artery demonstrating SFA and PA segments.