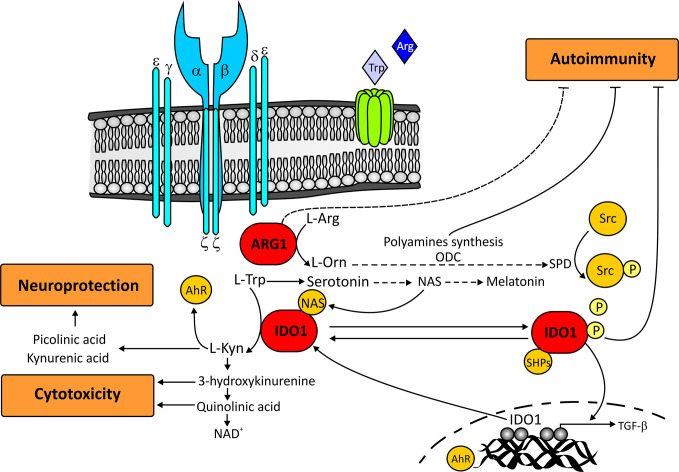
Figure 1.
Main IDO1 and ARG1-mediated pathways that regulate autoimmunity, cytotoxicity, and neuroprotection. The increase in ARG1 activity transforms L-Arginine into L-Ornithine, which is subsequently metabolized in the polyamine synthesis pathway. This metabolic pathway gives rise to spermine which, through the phosphorylation of Src kinase, facilitates the phosphorylation of IDO1. Once phosphorylated, IDO1 recruits tyrosine phosphatases, and promotes the upregulation of TGF-β and IDO1 coding genes. For its part, IDO1 catalyzes the conversion of L-Tryptophan into L-kynurenine which activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor further induces IDO1 expression and contributes to the production of polyamines through the stimulation of L-Ornithine metabolism. Together, the polyamine and IDO1 pathways, and probably ARG1, are capable of inhibiting the autoimmune response. L-Tryptophan through the kynurenine pathway is also capable of generating downstream metabolites both cytotoxic (3-hydroxykynurenine and quinolinic acid), and neuroprotective (picolinic acid and kynurenic acid). In addition to the Kynurenine pathway, Tryptophan is sequentially metabolized to serotonin, N-acetylserotonin, and melatonin. N-acetylserotonin acts as an allosteric modulator of IDO1, while melatonin contributes to the regulation of the autoimmune response by blocking the differentiation of Th17 cells and boosting the generation of protective Tr1 cells. For reasons of clarity in the figure, some of the participating routes have been omitted. Ahr, aryl hidrocarbon receptor; ARG1, Arginase1; IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; L-Arg, L-Arginine; L-Kyn, L-Kynurenine; L-Orn, L-Ornithine; L-Trp, L-Tryptophan; NAD, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NAS, N-acetylserotonin; ODC, ornithine decarboxylase; SHPs, tyrosine phosphatases; SPD, spermine; Src, Src kinase; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor-β.