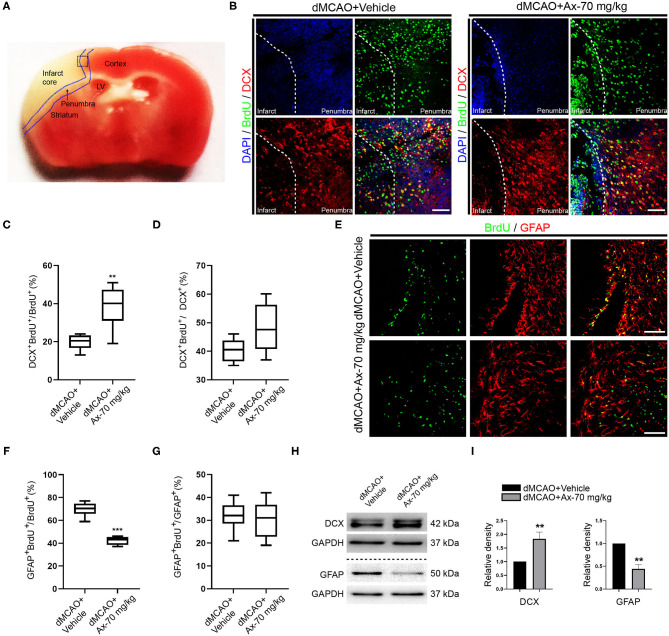
Figure 3.
Administration of 70 mg/kg Ax promotes NSCs differentiation into neurons and inhibits NSCs differentiation into astrocytes in penumbra after dMCAO. (A) Schematic illustration showing the regions after dMCAO: penumbra in blue dotted line; the black dotted square indicating region of interest (ROI) for immunostaining. (B) Representative immunostaining images showing colocalization of BrdU (green) and DCX (red) in ROI. DAPI was applied to counterstain the nuclei. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of DCX+ and BrdU+/BrdU+ in group dMCAO + Vehicle and dMCAO + Ax-70 mg/kg. **P < 0.01 vs. dMCAO + Vehicle group. (D) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of DCX+ and BrdU+/DCX+ in group dMCAO + Vehicle and dMCAO + Ax-70 mg/kg. (E) Typical immunostaining images showing colocalization of BrdU (green) and GFAP (red) in ROI. DAPI was applied to counterstain the nuclei. Scale bar: 20 μm. (F) Quantitation of the portion of GFAP+ and BrdU+/BrdU+ in group dMCAO + Vehicle and dMCAO + Ax-70 mg/kg. ***P < 0.001 vs. dMCAO + Vehicle group. (G) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of GFAP+ and BrdU+/GFAP+ in group dMCAO + Vehicle and dMCAO + Ax-70 mg/kg. (H) Immunoblot bands illustrating the expression of DCX and GFAP in penumbra in group dMCAO + Vehicle and dMCAO + Ax-70 mg/kg. GAPDH was served as an internal control. (I) Semi-quantitative analysis of the expression of DCX and GFAP in penumbra. **P < 0.01 vs. dMCAO + Vehicle group. Ax, ambroxol; dMCAO, distal middle cerebral artery occlusion; DCX, doublecortin; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; ROI, region of interest; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.