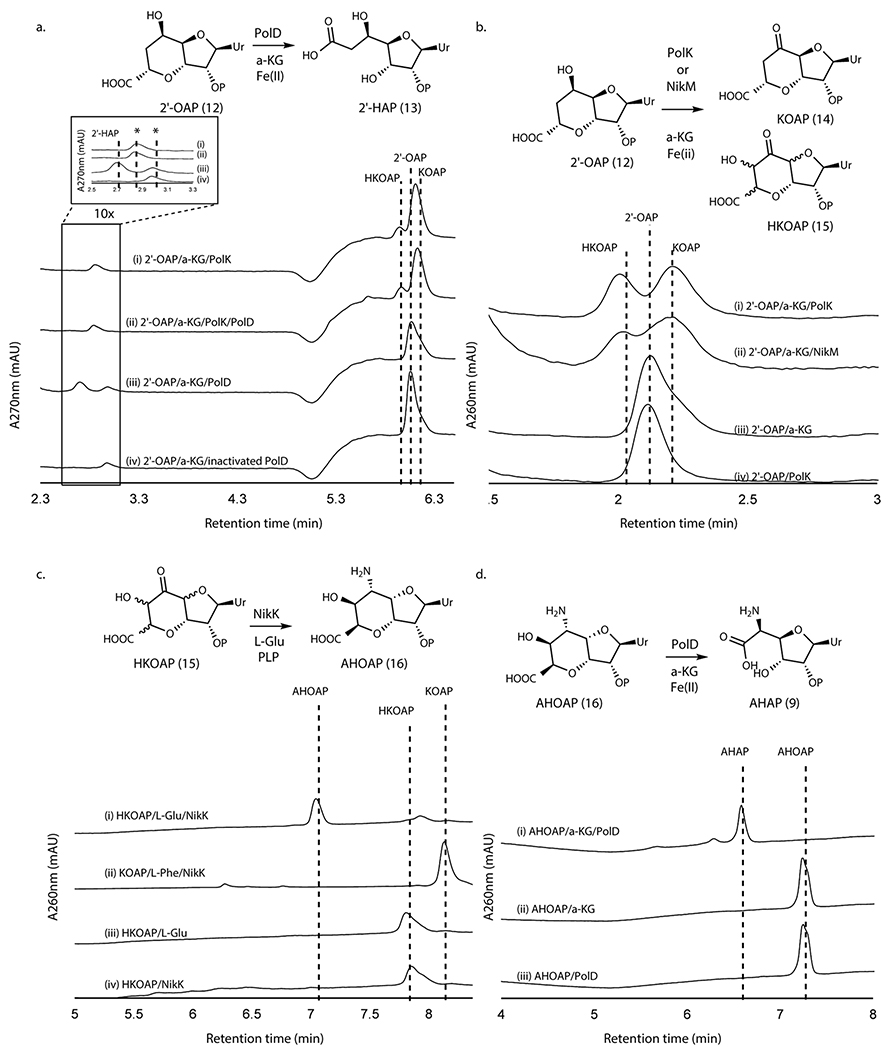
Figure 3. Transformation of 2’-OAP into AHAP.
a. PolK and PolD assays with 2’-OAP. Shown are HPAEC chromatograms at 270 nm for an assay with PolK (trace i), an assay with PolD and PolK (ii), an assay with PolD (iii), and a control with heat-inactivated PolD (iv). The peaks shown with asterisks are an unknown contaminant associated with both PolD and PolK, which has λmax at 247 nm and is not a uracil-related compound. b. PolK and NikM assays with 2’-OAP. Shown are HPAEC chromatograms at 260 nm for an assay with PolK (trace i), an assay with NikM (ii), a control without the enzyme (iii), and a control PolK assay without α-KG (iv). c. NikK assays with HKOAP or KOAP. Shown are HPAEC chromatograms at 260 nm for a NikK assay with HKOAP (trace i), a NikK assay with KOAP (scaled 1/6x) (ii), a control with HKOAP without NikK (iii), a control with HKOAP without l-Glu (iv). d. PolD assays with AHOAP. Shown are HPAEC chromatograms at 260 nm for the PolD assay in a complete condition (trace i), a control without the enzyme (ii), and a control without α-KG (iii). All enzyme activities were qualitatively reproducible in at least three independent assays in multiple different enzyme preparations.