Fig. 4 |. H1c/e deficiency reprograms H3K36me2 and H3K27me3 epigenome trajectories.
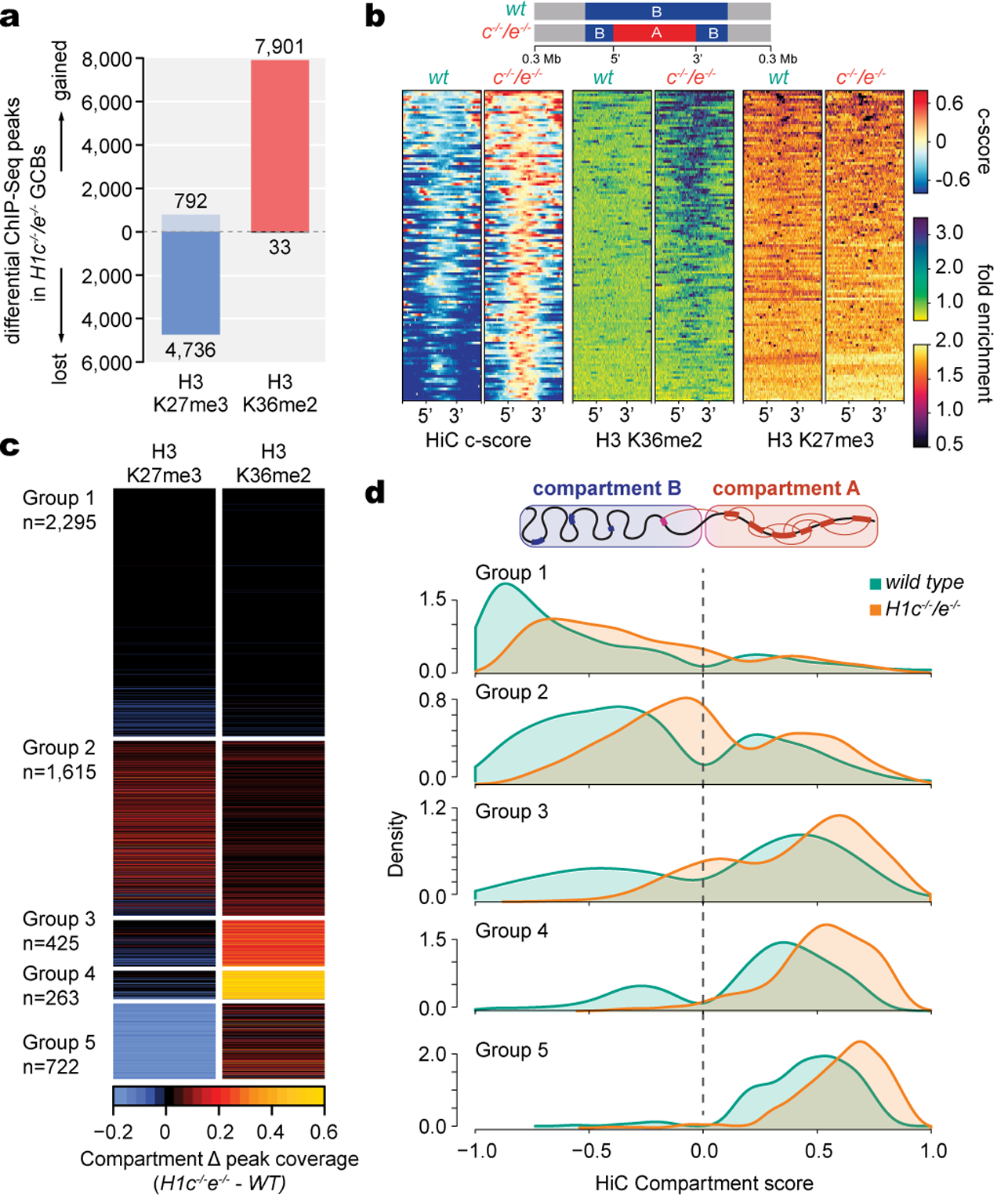
a, Differential ChIP-Seq peaks for H3K36me2 and H3K27me3 between H1c−/−/e−/− and wild-type GC B-cells (FC>1.5). b, Heatmap of compartment score, H3K36me2 and H3K27me3 fold enrichment centered within shifting B to A compartment “islands” (100 kb) and surrounding 300 kb in H1c−/−/e-/ -and wild-type GC B-cells. c, Heatmap of changing fraction peak coverage for H3K27me3 and H3K36me2 in H1c−/−/e−/− compared to wild-type H1 GC B-cells within decompacting compartments (n=5,320), subdivided into the five groups captured by unsupervised hierarchical clustering. d, Density plots showing the distribution of c-scores for shifting compartment groups 1–5 defined in (c) for H1c−/−/e−/−and wild-type H1C GC B-cells.
