Figure 3. Variants in mediators of meiotic arrest are associated with female infertility.
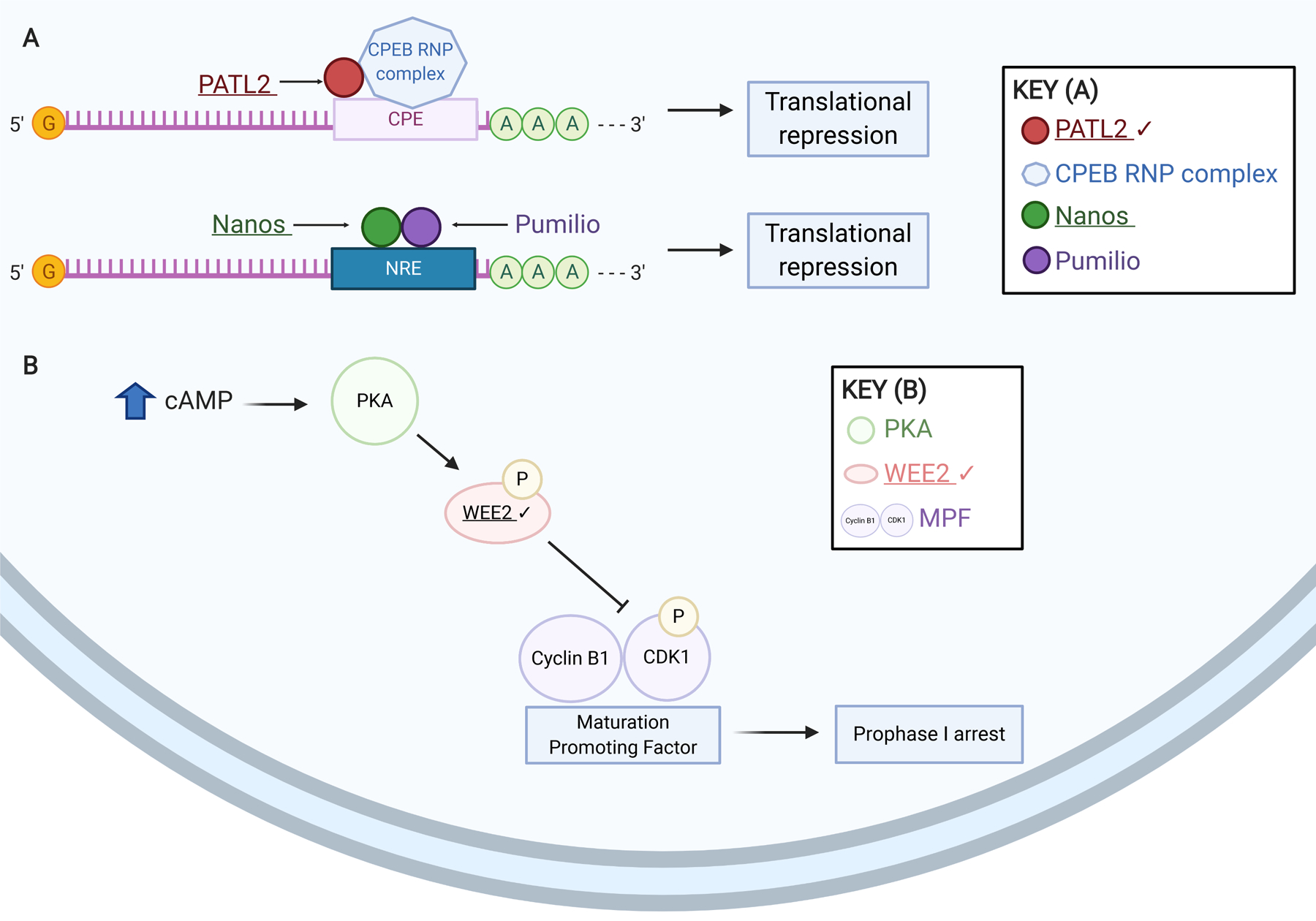
(A) Schematic of meiotic translational regulation mechanisms susceptible to infertility-causing genetic variants. Like PATL2, members of the Nanos family of proteins are recruited to a response element (NRE) in 3’ UTRs by Pumilio homolog(s) and repress translation of certain mRNAs. (B) Schematic of meiotic prophase I arrest mediators linked with female infertility. High cAMP levels trigger protein kinase A (PKA) phosphorylation of WEE2. Phosphorylated WEE2 in turn phosphorylates CDK1, which, with Cyclin B1, comprises the maturation promoting factor (MPF). This phosphorylation renders the MPF inactive and prophase I arrest is maintained. Exact stoichiometry is not depicted. Underlined gene products are implicated in infertility. Check marks (✔) indicate gene products discussed in this review. Created using BioRender.com.
