Figure 5. Exits from meiosis I and II are targets for infertility-causing genetic variants.
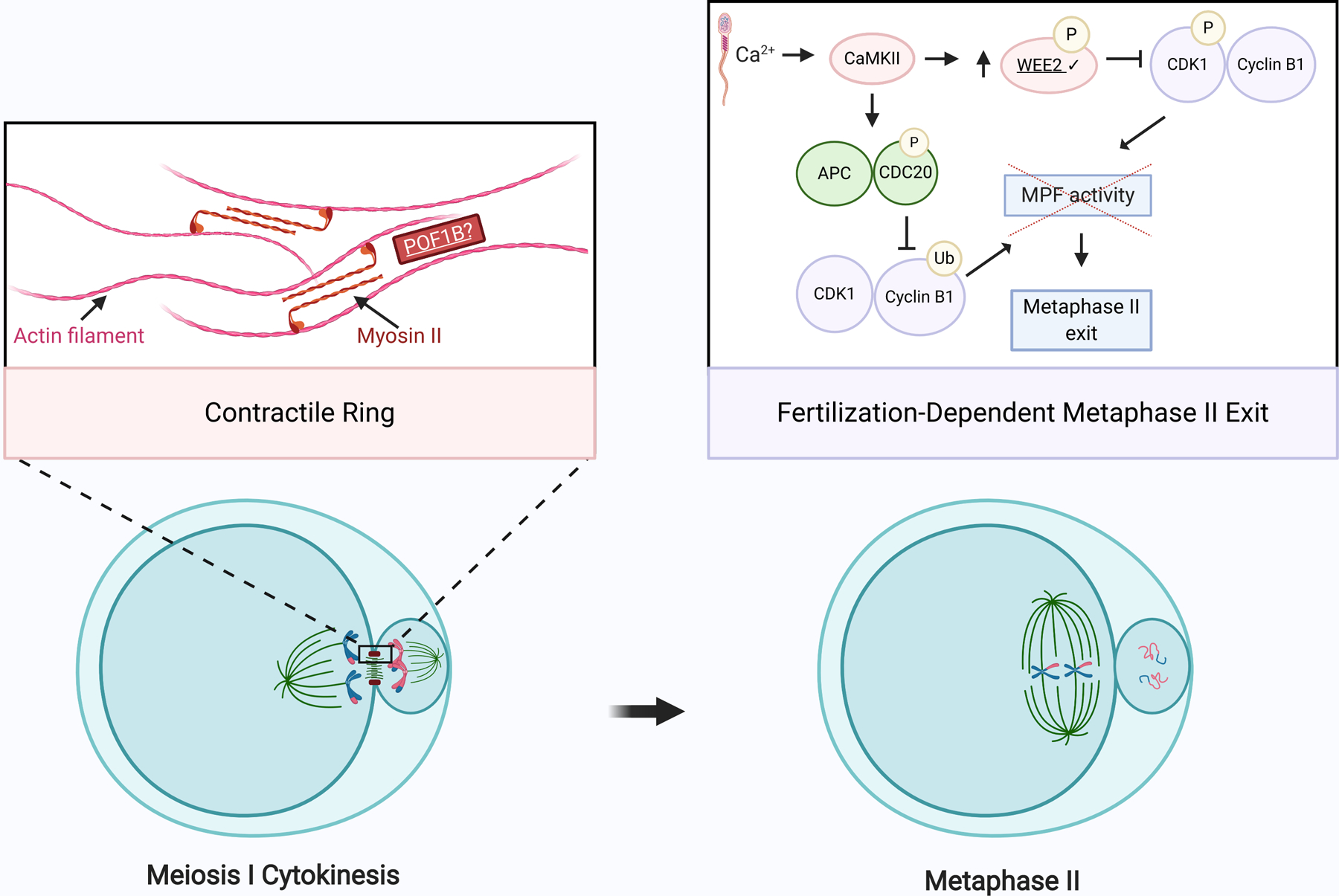
Schematic of meiosis I cytokinesis and meiosis II cell-cycle exit. During cytokinesis, actin filaments and myosin II form a contractile ring at the cleavage furrow. POF1B binds to non-muscle actin filaments and shares homology with myosin. Upon fertilization, an increase in intracellular calcium leads to activation of Ca2+/CaM-protein kinase II (CaMKII). CaMKII, in turn, activates WEE2 through phosphorylation. Activated WEE2 represses the maturation promoting factor (MPF), comprised of cyclin B1 and CDK1, by phosphorylating CDK1. This decrease in MPF activity, in concert with APC- and CDC20-mediated cyclin B1 decay, triggers exit from meiosis II. Exact stoichiometry is not depicted. Underlined gene products are implicated in infertility. Check marks (✔) indicate gene products discussed in this review. Created using BioRender.com.
