Figure 3: Drinking responses to 0.15 M saline.
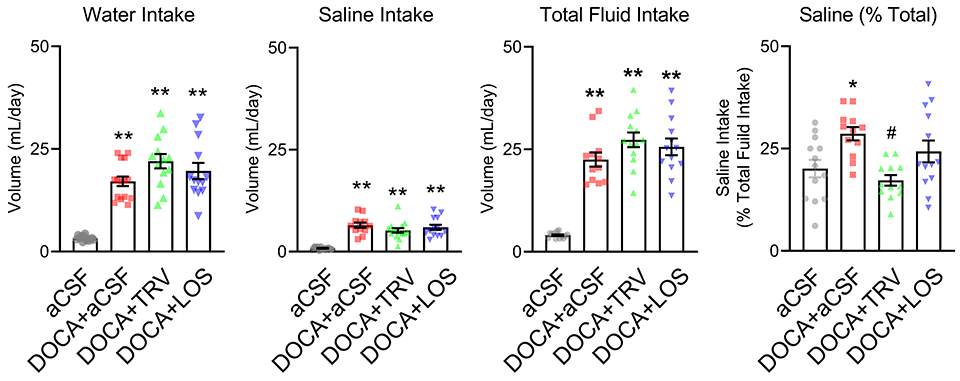
Control and mice subjected to DOCA with concomitant intracerebroventricular infusions of either artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF), TRV027, or losartan (LOS) were presented with a choice of tap water vs 0.15M NaCl (non-aversive saline). Total water intake, total saline intake, total fluid intake (calculated as total water intake plus total saline intake), and percentage of total intake from saline (calculated as total saline intake/total fluid intake x 100) are shown. All data are expressed as mean±SEM. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons procedure. *p<0.05 and **p<0.0001 compared with aCSF; #p<0.05 compared with DOCA+aCSF. N values are: aCSF (n=13), DOCA+aCSF (n= 15), DOCA+TRV027 (n=13), DOCA+LOS (n=13)
