Figure 2. Workflow for construction of the pooled doxycycline-inducible CRISPRi library.
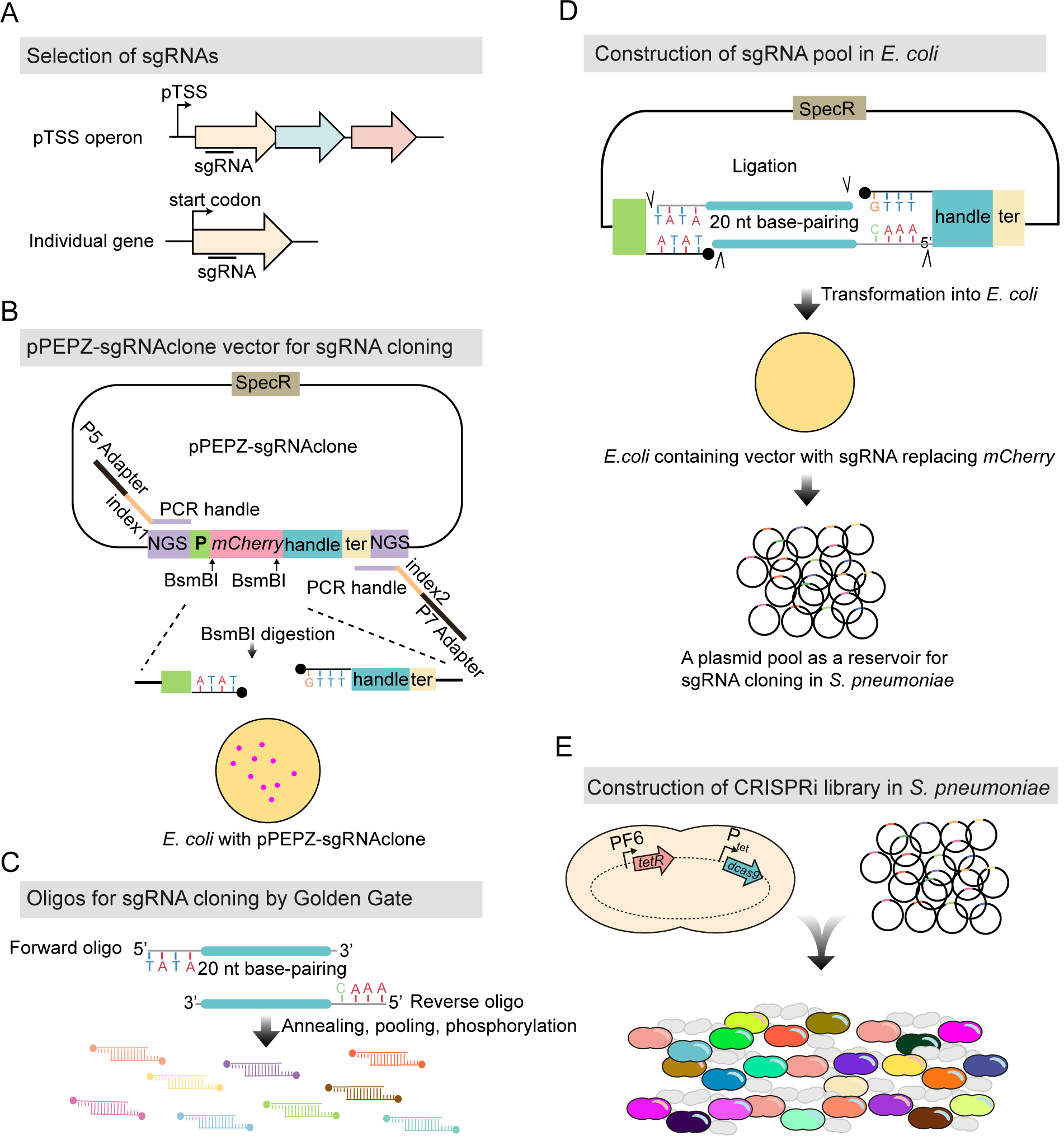
(A) 1499 sgRNAs were selected (see STAR methods), targeting 2111 genetic elements out of the 2146 in S. pneumoniae D39V. (B) The vector for sgRNA cloning, named pPEPZ-sgRNAclone, was designed to enable high efficiency Golden Gate cloning, monitoring false positive ratio, and construction of Illumina library in a one-step PCR. SpecR is the spectinomycin resistant marker; NGS indicates key elements which allow construction of an Illumina library by one-step PCR; P is the constitutive promoter which drives the expression of sgRNA; mCherry encodes a red fluorescent protein placed in the base-pairing region of sgRNA and flanked by a BsmBI site on each end; handle and ter represent the dCas9 handle binding region and terminator of the sgRNA. E. coli with the pPEPZ-sgRNAclone form red colonies resulting from the expression of mCherry. BsmBI digestion of the vector produces ends that are compatible with the sgRNA oligo annealing in (C). (C) Forward and reverse oligos were designed for each sgRNA containing 20 bp complementary to sgRNA and 4 nt overhangs compatible with the BsmBI digested vector. The oligos were annealed and pooled together followed by 5’ phosphorylation. (D) Ligation product of the digested vector (B) with the sgRNA annealing (C) was transformed into E. coli. E. coli transformed with the vector containing the sgRNA show white colonies due to replacement of mCherry with the sgRNA. 70,000 E. coli colonies were pooled together, and plasmids were purified and serve as an sgRNA reservoir. (E) Pooled plasmid library was transformed into a S. pneumoniae.
