Figure 5. CRISPRi-seq identified PurA as important for infection.
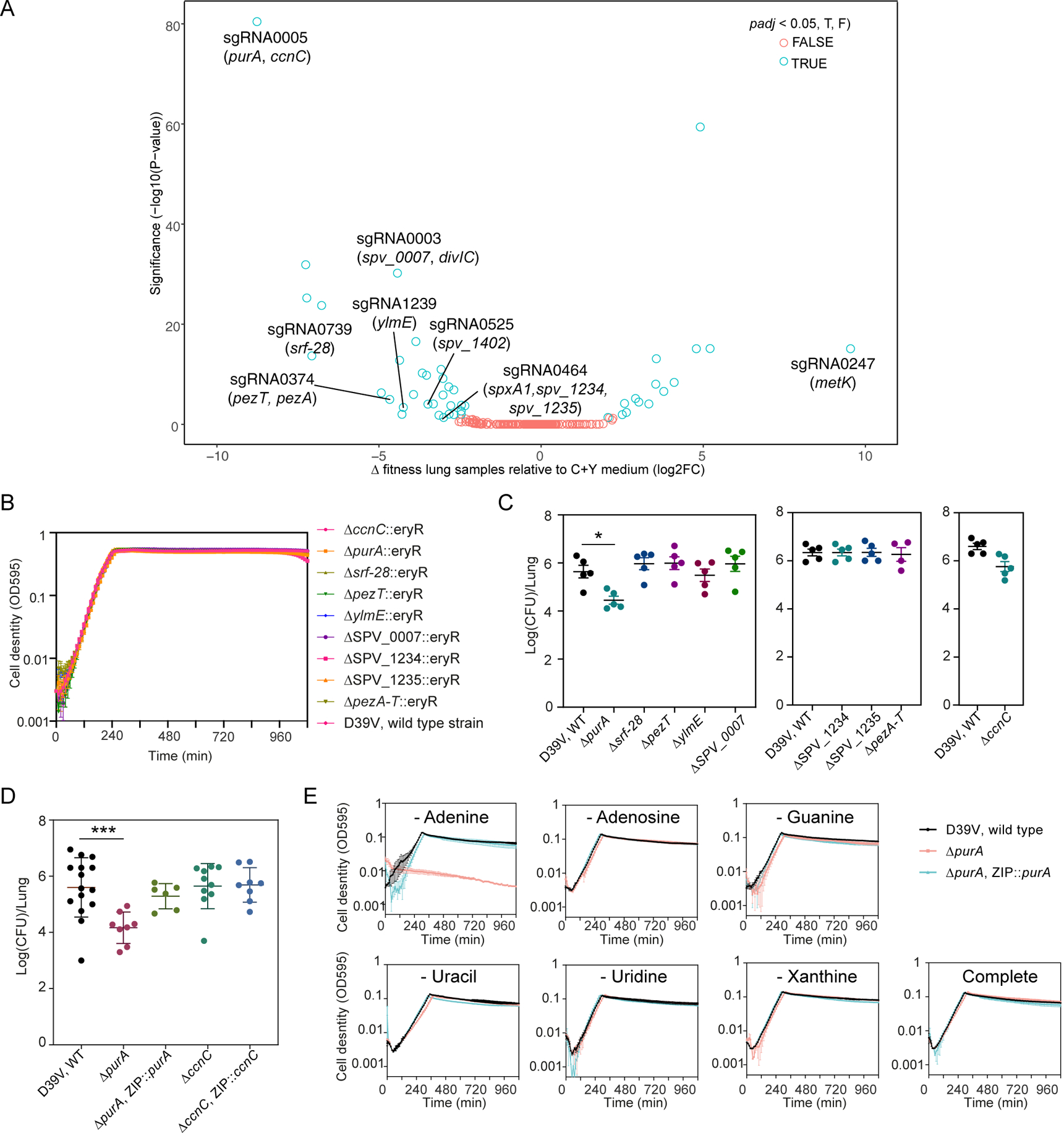
(A) Comparison of fitness cost of gene depletion by CRISPRi by different sgRNAs between the mouse lung infection model at 24 hpi and C+Y medium. The difference was shown as the log2 fold change between the two conditions by DEseq2 analysis and the P-values are adjusted by FDR. The highlighted sgRNAs were selected for follow-up studies. (B) Growth of the deletion mutants and the wild-type D39V strain in C+Y medium. Cell density was determined by measuring OD595nm every 10 minutes. The values represent averages of three technical replicates with SEM (same for panel E). (C-D) Mouse infection with individual mutants, compared to wild type D39V. Each dot represents a single mouse. Mean with SEM was plotted. (C) The mutants were tested in three batches of infection assays, for each assay the wild-type strain was tested in parallel. Significant difference between D39V and ΔpurA was tested by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, and the adjusted p value is 0.0158. (D) Validation study of sgRNA0005 targets. The virulence of deletion mutants and complementation strains were tested and compared to wild type D39V. There was a significant difference between the wild-type and ΔpurA strain tested by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-analysis, and the adjusted p-value was 0.0007. Note that ectopic expression of purA complemented the phenotype of the purA deletion mutant. (E) Growth of ΔpurA in blood-like medium lacking adenine, adenosine, guanine, uracil, uridine, xanthine, and complete medium.
