Figure 6. CRISPRi-seq in the influenza A virus pulmonary pneumococcal superinfection model.
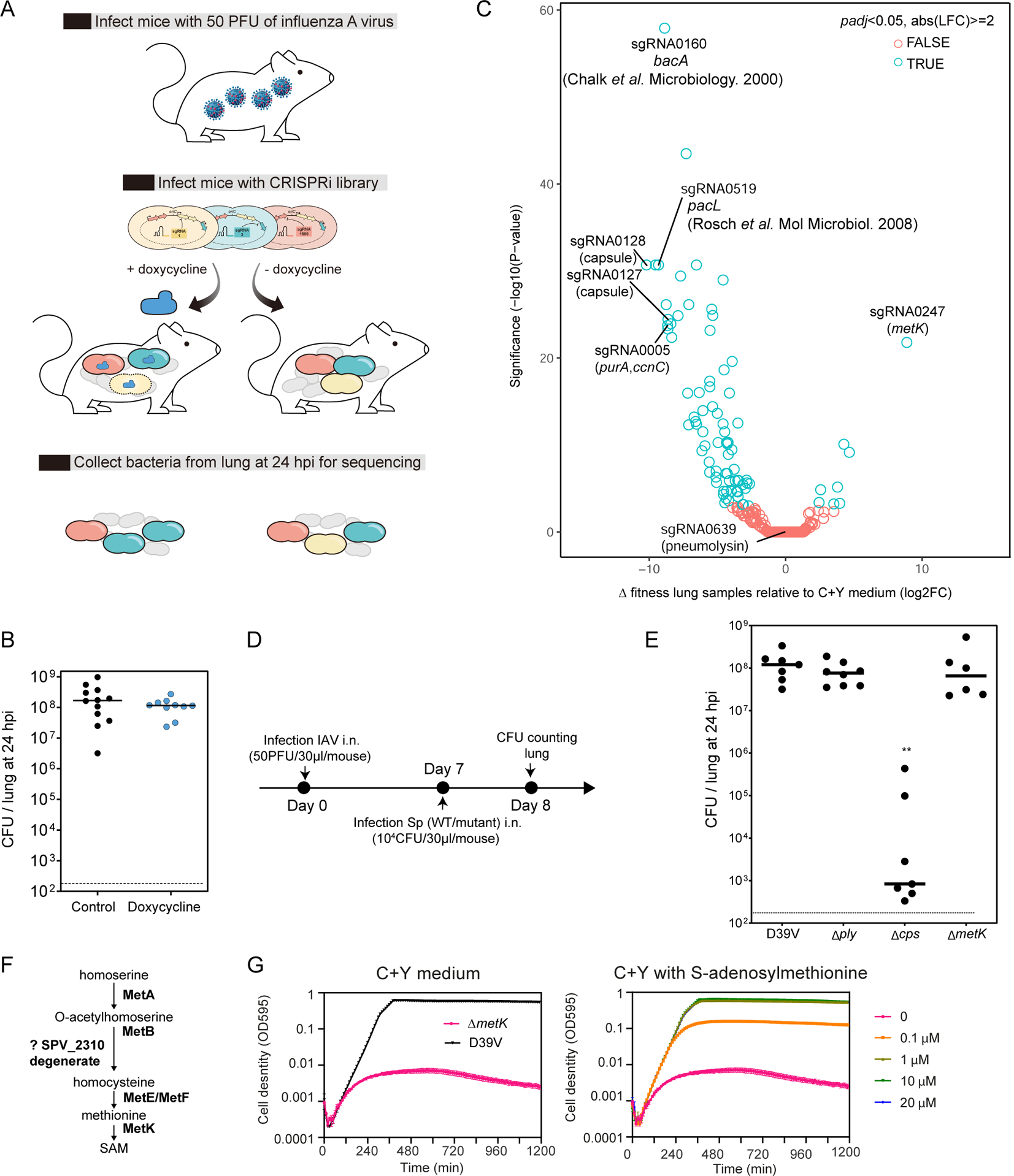
(A) Workflow of CRISPRi-seq screen. (B) The bacterial load in the lung at 24 hpi shows no impact of doxycycline. Horizontal bar indicates average. The inoculum used in this model is approximately 5×104 CFU intranasally (i.n.). (C) Comparison of fitness cost of gene between the IAV superinfection model at 24 hpi and C+Y medium. The difference was shown as the log2 fold change between the two conditions by DEseq2 analysis and the P-values are adjusted by FDR. Labelled circles represent sgRNAs targeting genes previously shown to be important for virulence or confirmed in the present study by mutational analysis. (D) Workflow for the confirmation study with individual strain in the IAV superinfection model. (E) IAV superinfection with pneumolysin deletion (Δply), capsule deletion (Δcps), and metK deletion (ΔmetK) mutant, compared to wild type D39V. Each dot represents a single mouse. ** indicate significantly different bacterial loads, p<0.05 Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA. Horizontal bar indicates average. (F) The biosynthetic pathway of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) synthesis. (G) Growth of the metK deletion mutant in C+Y medium supplemented with different concentrations of SAM. Mean and SEM of three replicates were shown. See also Figure S3.
