Figure 5.
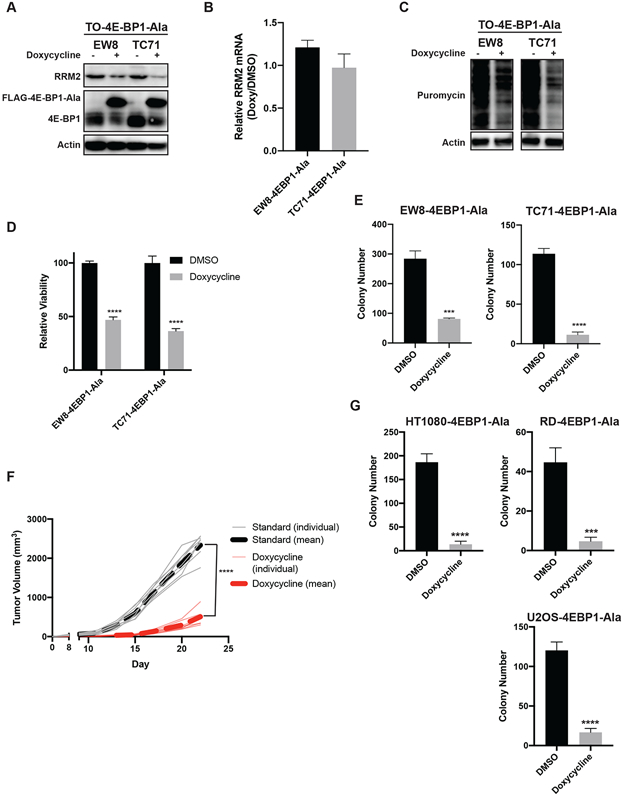
The inducible expression of constitutively-active 4E-BP1 reduces the level of the RRM2 protein and protein synthesis in sarcoma cells. (A) The doxycycline-inducible 4E-BP1-Ala cell lines were treated with doxycycline for 24 h. Cellular lysates were then collected for immunoblotting. (B) RT-qPCR for RRM2 mRNA in the 4E-BP1-Ala cell lines treated with doxycycline or DMSO for 24 h. (C) The doxycycline-inducible 4E-BP1-Ala cell lines were treated with doxycycline for 24 h. Cells were labeled with puromycin to quantify protein synthesis and then lysates were collected for immunoblotting. (D) The 4E-BP1-Ala cell lines were treated with doxycycline or DMSO for 72 h. Cell viability was then quantified using the AlamarBlue assay. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of three technical replicates. The results are representative of two independent experiments. (E) The 4E-BP1-Ala cell lines were treated with doxycycline or DMSO for 14 days and then the number of colonies were counted. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of three technical replicates. (F) TC71 cells with doxycycline-inducible expression of 4E-BP1-Ala were implanted subcutaneously (Day 0) in NCr mice. Mice were then fed standard chow (n=8) or doxycycline-containing chow (n=8). Tumor size was quantified every 2-3 days using caliper measurements. The plot shows the tumor growth for the individual mice, as well as the mean tumor volume (dotted line) for the mice receiving standard or doxycycline-containing chow. (G) HT1080, RD, and U2OS doxycycline-inducible 4E-BP1-Ala cell lines were treated with doxycycline for 24 h. Cells were labeled with puromycin to quantify protein synthesis and then lysates were collected for immunoblotting. Protein loading for all of the immunoblots was normalized using cell number.
