Figure 5. EPAC activity contributes to hyperexcitability induced by 5-HT.
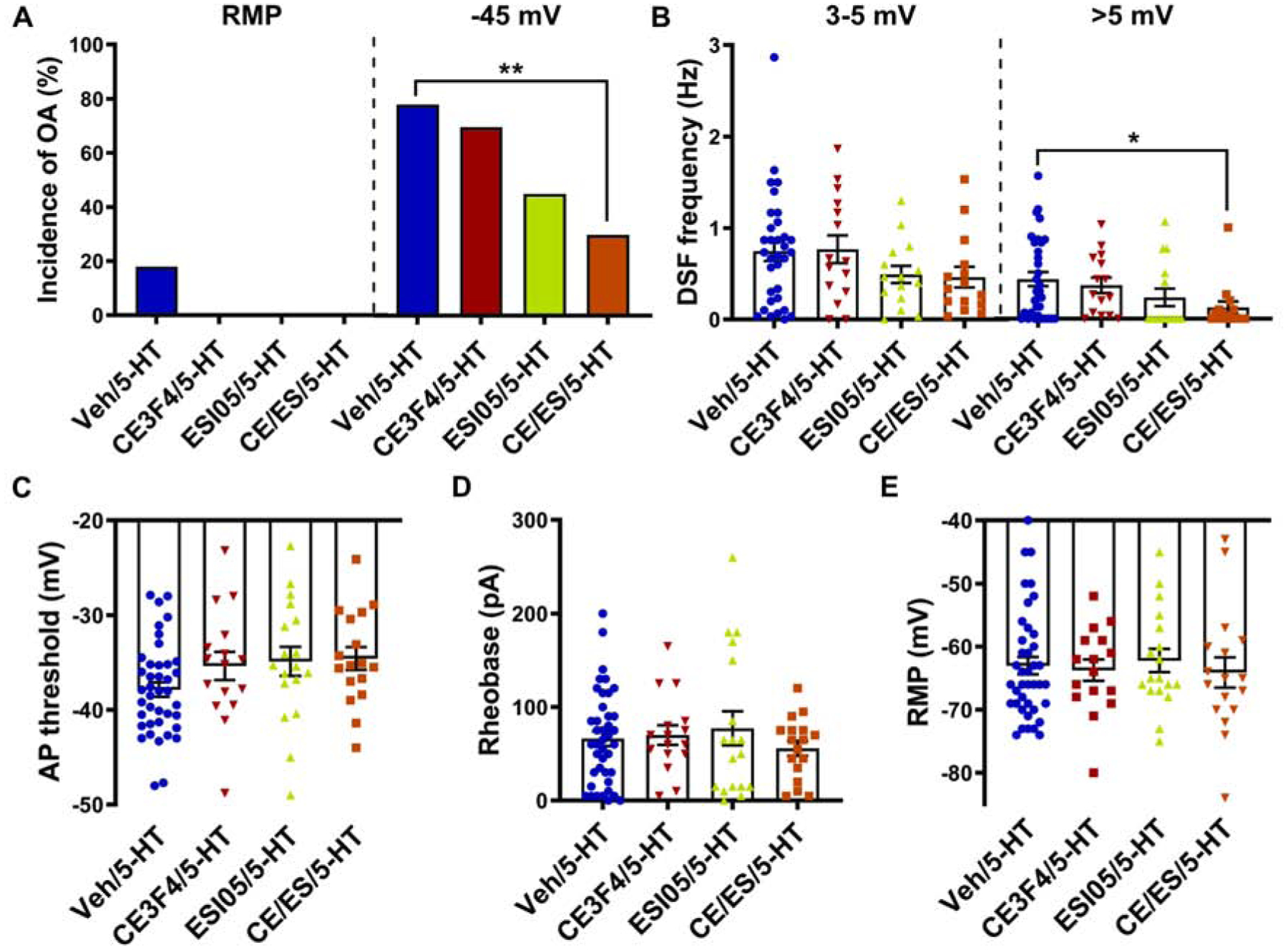
Cells were treated with CE3F4 (10 μM) or ESI-05 (5 μM) alone or in combination or vehicle control before and during exposure to 100–300 nM 5-HT. (A) Effects of EPAC inhibitors on the incidence of OA was measured during ≥60-s recordings at RMP then during 30-s depolarization to −45 mV in the presence of 5-HT. ** p < 0.0033 (Bonferroni correction for 3 comparisons). (B) Effects of EPAC inhibitors on the frequency of medium- (3–5 mV) and large-amplitude (>5 mV) DSFs during 30-s depolarization to −45 mV in the presence of 5-HT. Mean ± SEM. * Dunn’s adjusted p value < 0.05. (C) Effects of EPAC inhibitors on the AP voltage threshold during exposure to 5-HT. Mean ± SEM. (D, E) Effects of EPAC inhibitors on rheobase (D) and RMP (E) during exposure to 5-HT.
