Figure 2: Food intake and activity levels are decreased in males challenged with diet induced obesity.
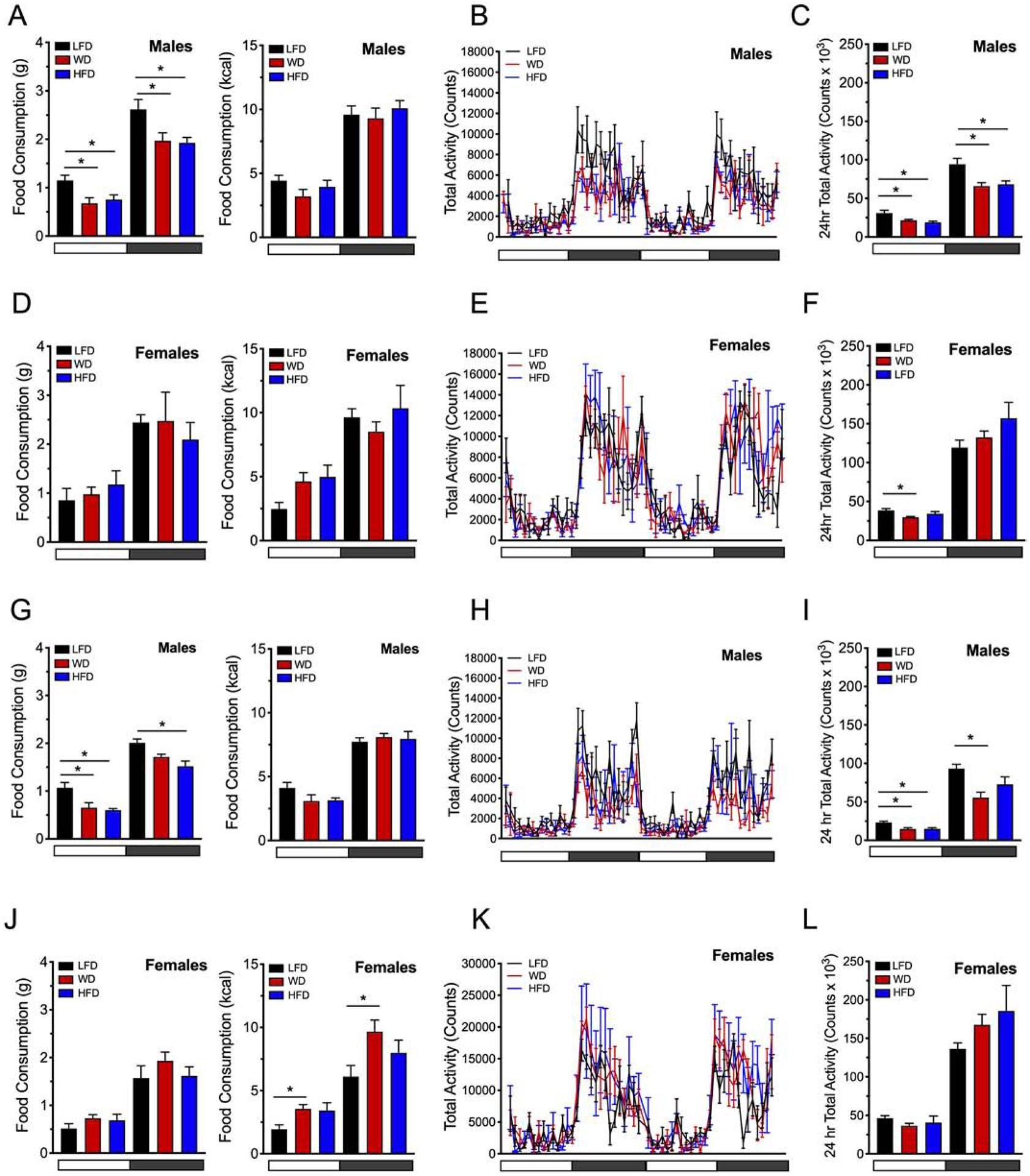
Male and female C57BL6/J mice were placed on a dietary intervention starting at 4 weeks of age. Food intake was monitored and activity was assessed by recording the number of beam breaks occurring in the x + y- and z-axes at 8 and 16 weeks of diet. (A) Food intake of male mice at 8 weeks of dietary intervention shown in grams/12 hr cycle (left panel) and as kcal/12 hr cycle (right panel); (B) Male locomotor activity during the light and dark cycles at 8 weeks of dietary intervention (48 hours depicted); (C). Male locomotor activity at 8 weeks of dietary intervention (total beam break counts in 24 hours); (D) Food intake of female mice at 8 weeks of dietary intervention shown in grams/12 hr cycle (left panel) and as kcal/12 hr cycle (right panel); (E) Female locomotor activity during the light and dark cycles at 8 weeks of dietary intervention (48 hours depicted); (F). Female locomotor activity at 8 weeks of dietary intervention (total beam break counts in 24 hours); (G) Food intake of male mice at 16 weeks of dietary intervention shown in grams/12 hr cycle (left panel) and as kcal/12 hr cycle (right panel); (H) Male locomotor activity during the light and dark cycles at 16 weeks of dietary intervention; (I) Male locomotor activity at 16 weeks of dietary; (J) Food intake of female mice at 16 weeks of dietary intervention shown in grams/12 hr cycle (left panel) and as kcal/12 hr cycle (right panel); (K) Female locomotor activity during the light and dark cycles at 16 weeks of dietary intervention; (L) Female locomotor activity at 16 weeks of dietary intervention. Horizontal white bars denote light cycles (0700 – 1900) and dark gray horizontal bars denote dark cycles (1900 – 0700). Results are displayed as means ± SEM; Means were compared by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posttest; *, p<0.05, n=9–10.
