Figure 3. Different domains of Cep70 contribute to different cellular localizations.
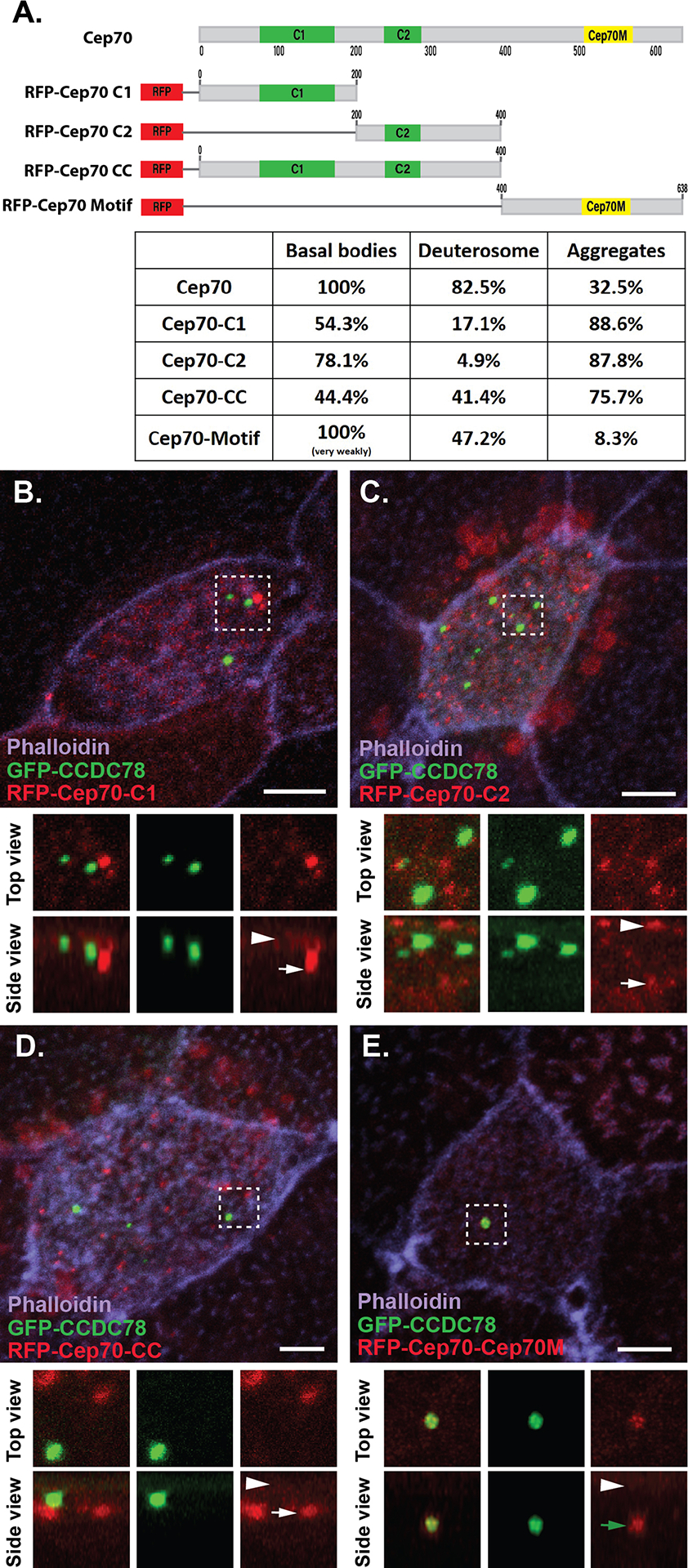
A, Domain map of Cep70 and description of the 4 individual domain constructs used in B-E along with quantification of localization for each construct (n > 30 cells for each condition). Scale bars are 5μm. B–E, Localization of GFP-CCDC78 (green) and RFP-Cep70 (red) domain constructs in mature MCCs stained with phalloidin (purple) with boxed areas blown up and shown without phalloidin both top and side projections. B, RFP-Cep70-C1 localizing weakly at the level of basal bodies (arrowhead) and in cytoplasmic aggregates (white arrow). C, RFP-Cep70-C2 localizing strongly at the level of basal bodies (arrowhead) and in cytoplasmic aggregates (white arrow). D, RFP-Cep70-CC localizing weakly at the level of basal bodies (arrowhead) and in cytoplasmic aggregates (white arrow). E, RFP-Cep70-Cep70M localizing very weakly at the level of basal bodies (arrowhead) and at the deuterosome (green arrow).
