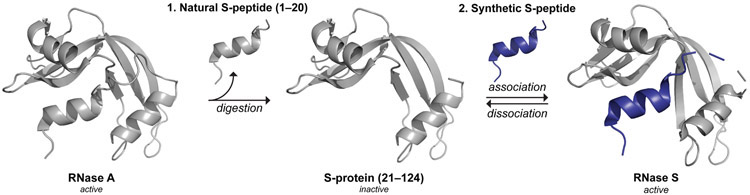
Figure 1.
Traditional production of semisynthetic RNase S. Step 1: Proteolytic digestion of RNase A to cleave S-peptide (residues 1–20) and yield catalytically inactive S-protein (residues 21–124). Step 2: Reversible association of S-protein and a synthetic S-peptide variant to produce catalytically active, semisynthetic RNase S. Images were produced with PyMOL software and PDB entries 1jvt21 and 1rnu.22