Fig. 4.
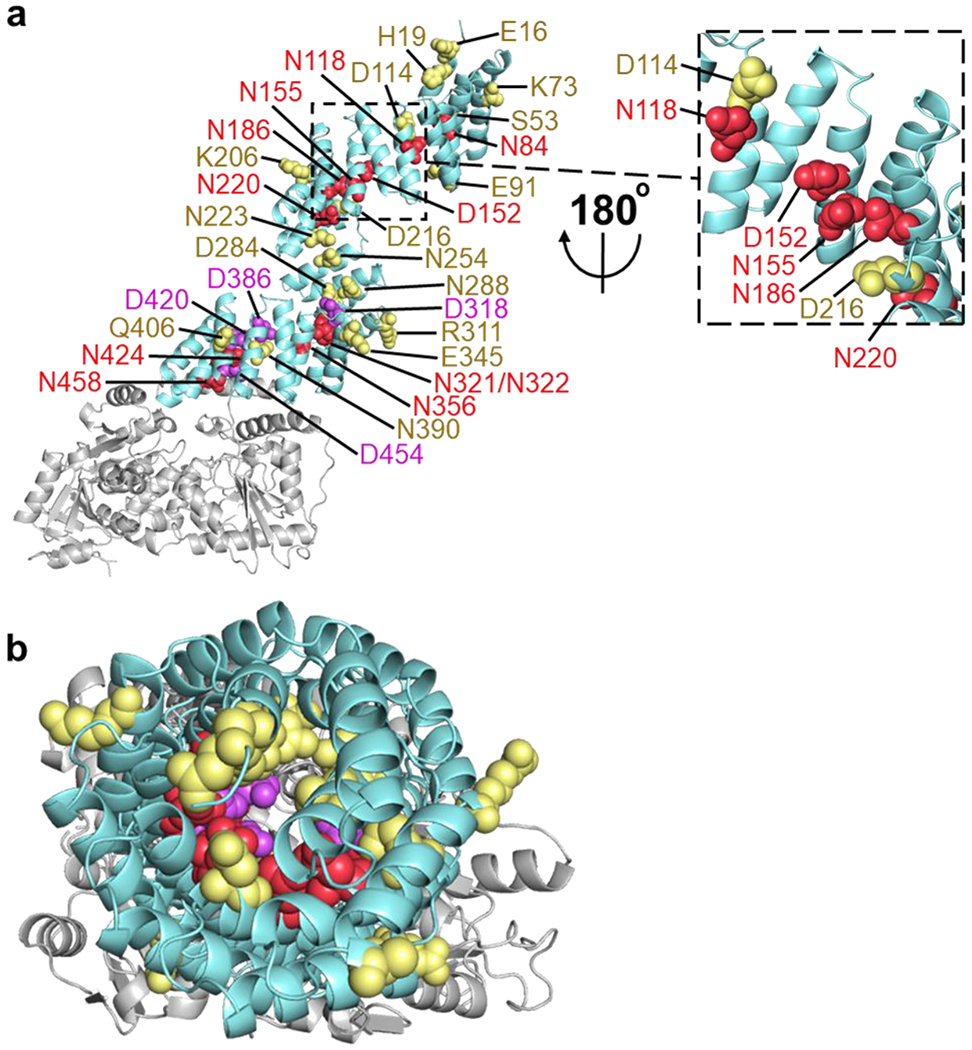
Inner asparagine and aspartate residues extending throughout OGT TPR lumen regulate OGA glycosylation. (a) Full-length human OGT structure was generated by overlaying the crystal structures of OGT4.5 (PDB code 3PE3) [52] and the first 11.5 TPRs (PDB code 1W3B) [51]. Residues that facilitated protein binding and/or sugar transfer for OGA are shown as red spheres, while residues that hindered protein binding and/or sugar transfer for OGA are colored purple. Functionally disposable residues for the glycosylation of full-length OGA are depicted as yellow spheres. (b) Top-down (N-terminal to C-terminal) view of the same OGT model and coloring as a.
