FIGURE 3.
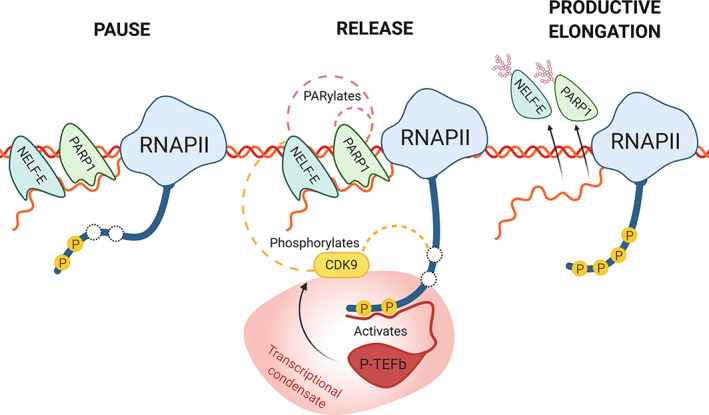
PARP1's role in transcription elongation. During RNAPII pausing, a chromatin associated PARP1 assists NELF by binding to the nascent pre‐mRNA. Partial phosphorylation of RNAPII carboxy‐terminal domain (CTD) recruits the low complexity region of P‐TEFb, activating CDK9 (reviewed in Thomas et al. (2019)). To release RNAPII, CDK9 then hyperphosphorylates RNAPII's CTD and also phosphorylates NELF‐E. Phosphorylation of NELF‐E then instigates PARylation of NELF‐E by PARP1, which is also autoPARylated. PARylation of NELF‐E and PARP1 inhibit their RNA‐binding, releasing both proteins from the nascent pre‐mRNA, and allowing the RNAPII complex to enter productive elongation. Splicing condensate is shown as the reddish structure
