Figure 4. R59X/+ female mice present with epileptic spasms.
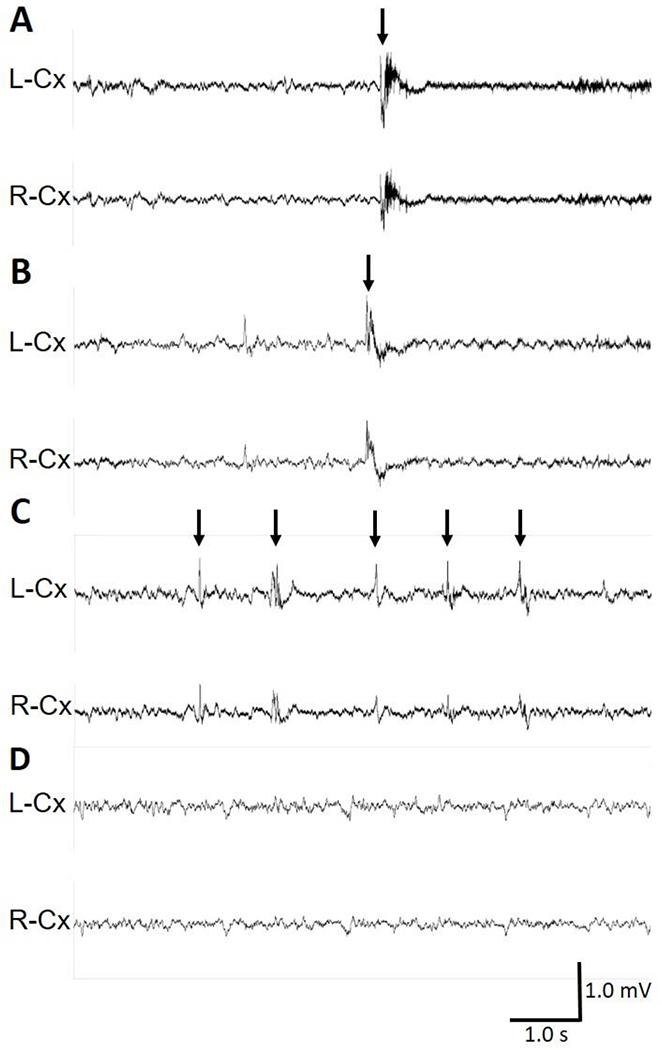
(A-D) Representative 10-s traces of intracranial EEG recorded in wild-type (+/+) and R59X/+ female mice. (A) Epileptic spasm in a R59X/+ heterozygous female mouse occurring during sleep, characterized by bilateral sharp-wave activity. Also see Supplementary Video 6 of this event. (B) Epileptic spasm in a different R59X/+ heterozygous female mouse occurring during sleep, characterized by bilateral spike/polyspike-wave activity. Also see Supplementary Video 7 of this event. (A-B) Arrows indicate time of spasm onset. (C) Interictal spiking during a period of behavioral arrest in a R59X/+ mouse. Arrows indicate interictal spikes. (D) Normal EEG during sleep in a wild type mouse. Vertical scale bar represents 1 mV. Horizontal scale bar represents 1.0 s in all traces. L-Cx: left cortical lead, R-Cx: right cortical lead.
