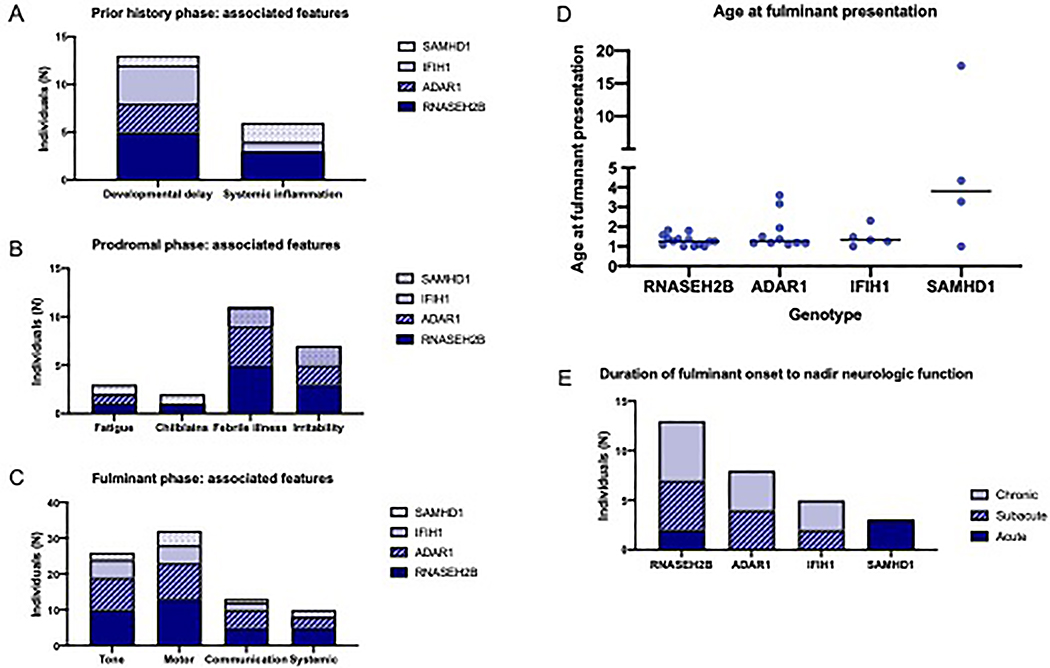
Figure 2.
Common features of the phases of atypical AGS by genotype. The most common clinical features during each phase were noted by genotype in non-exclusive categories. (A) In the early phase, developmental delay and systemic inflammation were most commonly noted; (B) in the prodrome phase, fatigue, irritability, sterile pyrexias (febrile illnesses), and chilblains were noted; while in the fulminant phase (C), abnormalities in tone, motor skills, communication, and systemic signs or symptoms were most common. (D) The age at fulminant presentation is presented by genotypic cohort. (E) The time to neurologic nadir (maximum symptoms) was categorized as acute (within a week), subacute (1 week to 1 month), or chronic (more than 1 month).