Figure 1.
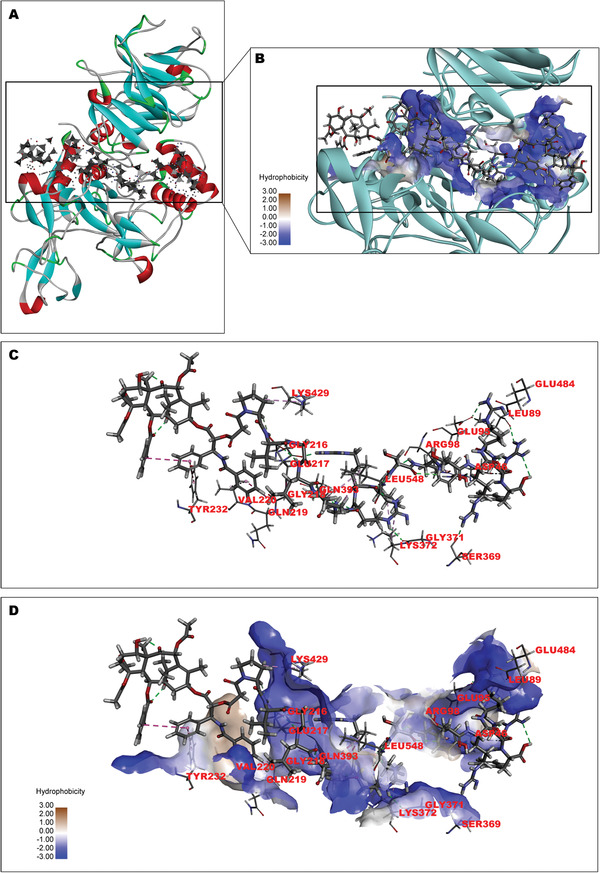
Interaction and the binding pattern of SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX and MMP‐2. The structure of MMP‐2 in this study was collected from the RCSB PDB (ID: 1CK7). A) The binding poses of MMP‐2 (the ribbon structure) with SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX (−151.29 kcal mol−1). In the structure of MMP‐2, β‐sheet (blue), loop (gray), α‐helix (red), and the amino acid structure connecting different segments (green) are demonstrated. The gray structure with the spots and surfaces represents SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX. B) The graph of partial enlargement shows the binding site of MMP‐2 (ribbon and sphere) and SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX. The cyan ribbon and the blue spheres represent MMP‐2 and its hydrophilic binding region, respectively. In the structure of SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX, the carbon (C), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N) and hydrogen (H) are represented by dark‐gray, red, blue, and light‐gray balls, respectively. C) The 3D structure between SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX and corresponding amino residue of MMP‐2 is shown. Gray dashed lines represent the hydrogen bond interactions between SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX and MMP‐2. D) The interaction mode of SynB3‐PVGLIG‐PTX with MMP‐2 is presented, where the hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues are labeled.
