Figure 6.
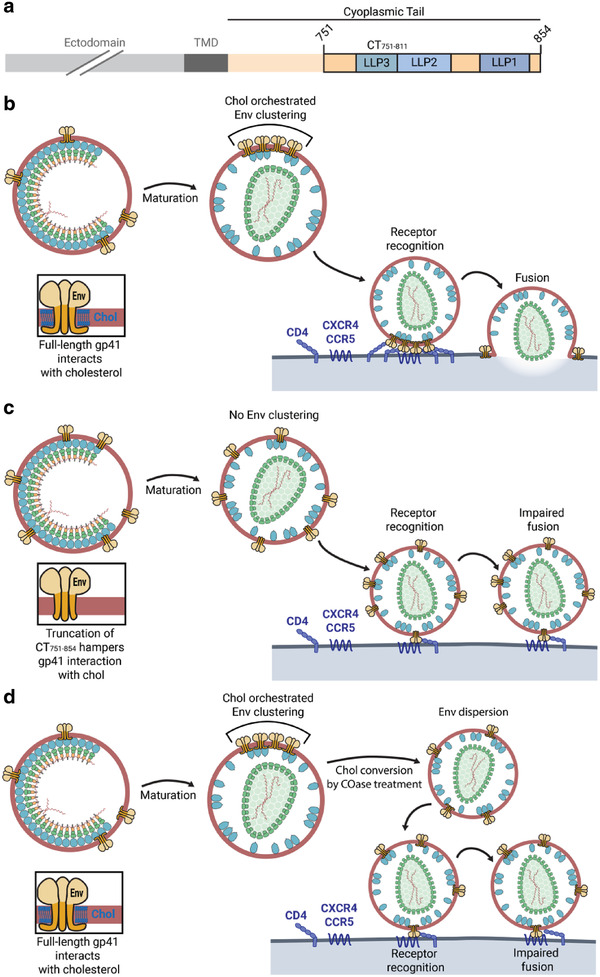
Env clustering depends on CT751–811 mediated chol interaction and maturation state. a) Schematic illustration of the CT751–854 region responsible for gp41–chol interaction. b) In wild‐type HIV‐1 particles, the full‐length gp41 protein interacts with viral membrane chol via the CT751–854 region. Upon maturation, Env trimers are free to diffuse and coalesce into a single focus mediated by their interaction with chol. This clustering enables efficient fusion with the host cell. c) When the CT751–854 region is truncated, the protein loses the capacity to interact with chol. Upon maturation, truncated Env trimers cannot coalesce into a single focus as they are excluded from chol‐rich domains. The absence of an Env cluster results in a defect in fusion with the host cell. d) Disruption of the gp41–chol interaction by treatment of wild‐type HIV‐1 particles with COase and conversion of chol to cholestenone, induces a dispersion of the already clustered Env particles, resulting in a phenotype similar to the truncated Env trimers.
