Figure 6.
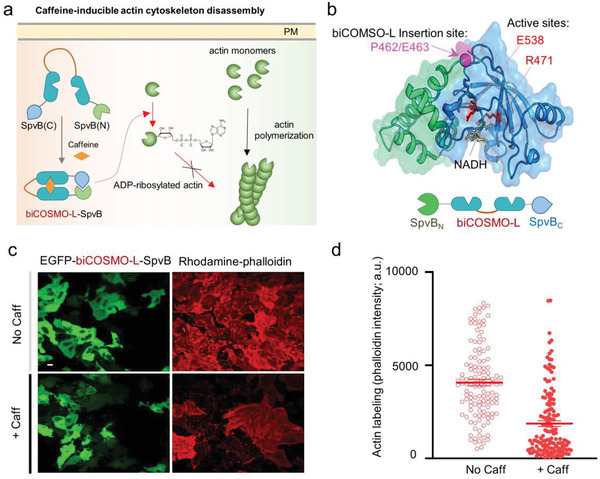
Design of a caffeine‐switchable, genetically encoded inhibitor of actin cytoskeleton assembly based on biCOSMO‐L. a) Schematic illustration of caffeine‐inducible actin cytoskeleton disassembly. biCOSMO‐L is inserted between SpvB (N) (aa 375–462) and SpvB (C) (aa 463–591). b) The 3D structure of an ADP‐ribosyltransferase (ATR) domain derived from Salmonella SpvB (PDB entry: 3GWL). The domain architecture of the construct was shown below the cartoon. Green, SpvB_ATR N‐domain; blue, SpvB_ATR C‐domain; magenta, biCOSMO‐L insertion site between P461 and E462; red, active sites that catalyze actin ADP ribosylation using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as substrate. c) Confocal images showing EGFP–biCOSMO‐L–SpvB‐expressing HeLa cells (green) stained with rhodamine‐conjugated phalloidin (red) before and after caffeine treatment. d) Quantification of phalloidin staining results before and after caffeine treatment (as shown in panel (c)). n = 130–150 cells from three independent assays.
